Derivative of Extremophilic 50S Ribosomal Protein L35Ae as an Alternative Protein Scaffold
- PMID: 28103321
- PMCID: PMC5245882
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170349
Derivative of Extremophilic 50S Ribosomal Protein L35Ae as an Alternative Protein Scaffold
Abstract
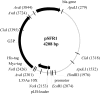
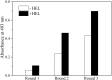
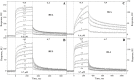
Small antibody mimetics, or alternative binding proteins (ABPs), extend and complement antibody functionality with numerous applications in research, diagnostics and therapeutics. Given the superiority of ABPs, the last two decades have witnessed development of dozens of alternative protein scaffolds (APSs) for the design of ABPs. Proteins from extremophiles with their high structural stability are especially favorable for APS design. Here, a 10X mutant of the 50S ribosomal protein L35Ae from hyperthermophilic archaea Pyrococcus horikoshii has been probed as an APS. A phage display library of L35Ae 10X was generated by randomization of its three CDR-like loop regions (repertoire size of 2×108). Two L35Ae 10X variants specific to a model target, the hen egg-white lysozyme (HEL), were isolated from the resulting library using phage display. The affinity of these variants (L4 and L7) to HEL ranges from 0.10 μM to 1.6 μM, according to surface plasmon resonance data. While L4 has 1-2 orders of magnitude lower affinity to HEL homologue, bovine α-lactalbumin (BLA), L7 is equally specific to HEL and BLA. The reference L35Ae 10X is non-specific to both HEL and BLA. L4 and L7 are more resistant to denaturation by guanidine hydrochloride compared to the reference L35Ae 10X (mid-transition concentration is higher by 0.1-0.5 M). Chemical crosslinking experiments reveal an increased propensity of L4 and L7 to multimerization. Overall, the CDR-like loop regions of L35Ae 10X represent a proper interface for generation of functional ABPs. Hence, L35Ae is shown to extend the growing family of protein scaffolds dedicated to the design of novel binding proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
Antherix and Biomirex Inc. provided support in the form of salary for author TAM. This does not alter the authors' adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Extremophilic 50S Ribosomal RNA-Binding Protein L35Ae as a Basis for Engineering of an Alternative Protein Scaffold.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 6;10(8):e0134906. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134906. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26247602 Free PMC article.
-
Solution NMR structure of the ribosomal protein RP-L35Ae from Pyrococcus furiosus.Proteins. 2012 Jul;80(7):1901-6. doi: 10.1002/prot.24071. Epub 2012 Apr 16. Proteins. 2012. PMID: 22422653 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the DUF54 family protein PH1010 from hyperthermophilic archaea Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3.Proteins. 2009 Jan;74(1):256-60. doi: 10.1002/prot.22255. Proteins. 2009. PMID: 18831045 No abstract available.
-
Structure of a two-domain N-terminal fragment of ribosomal protein L10 from Methanococcus jannaschii reveals a specific piece of the archaeal ribosomal stalk.J Mol Biol. 2010 Jun 4;399(2):214-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.04.017. Epub 2010 Apr 24. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20399793 Review.
-
Structure and function of archaeal prefoldin, a co-chaperone of group II chaperonin.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2010 Jan 1;15(2):708-17. doi: 10.2741/3641. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2010. PMID: 20036841 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

