Dynamic Interaction between Reinforcement Learning and Attention in Multidimensional Environments
- PMID: 28103483
- PMCID: PMC5287409
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.12.040
Dynamic Interaction between Reinforcement Learning and Attention in Multidimensional Environments
Abstract
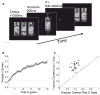
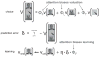
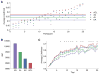
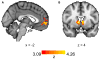
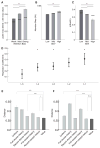
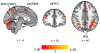
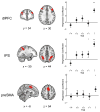
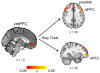
Little is known about the relationship between attention and learning during decision making. Using eye tracking and multivariate pattern analysis of fMRI data, we measured participants' dimensional attention as they performed a trial-and-error learning task in which only one of three stimulus dimensions was relevant for reward at any given time. Analysis of participants' choices revealed that attention biased both value computation during choice and value update during learning. Value signals in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex and prediction errors in the striatum were similarly biased by attention. In turn, participants' focus of attention was dynamically modulated by ongoing learning. Attentional switches across dimensions correlated with activity in a frontoparietal attention network, which showed enhanced connectivity with the ventromedial prefrontal cortex between switches. Our results suggest a bidirectional interaction between attention and learning: attention constrains learning to relevant dimensions of the environment, while we learn what to attend to via trial and error.
Keywords: MVPA; attention; computational modeling; decision making; fMRI; prediction error; reinforcement learning; striatum; value; vmPFC.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bellman R. Dynamic Programming. Princeton University Press; 1957.
-
- Botvinick MM. Hierarchical reinforcement learning and decision making. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2012;22:956–962. - PubMed
-
- Brainard DH. The psychophysics toolbox. Spat Vis. 1997;10:433–436. - PubMed
-
- Corbetta M, Shulman GL. Control of goal-directed and stimulus-driven attention in the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3:201–215. - PubMed
-
- Corbetta M, Akbudak E, Conturo TE, Snyder AZ, Ollinger JM, Drury HA, Linenweber MR, Petersen SE, Raichle ME, Van Essen DC, Shulman GL. A common network of functional areas for attention and eye movements. Neuron. 1998;21:761–773. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

