Identification of aurintricarboxylic acid as a selective inhibitor of the TWEAK-Fn14 signaling pathway in glioblastoma cells
- PMID: 28103571
- PMCID: PMC5355340
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14685
Identification of aurintricarboxylic acid as a selective inhibitor of the TWEAK-Fn14 signaling pathway in glioblastoma cells
Abstract
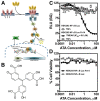
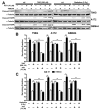
The survival of patients diagnosed with glioblastoma (GBM), the most deadly form of brain cancer, is compromised by the proclivity for local invasion into the surrounding normal brain, which prevents complete surgical resection and contributes to therapeutic resistance. Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK), a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily, can stimulate glioma cell invasion and survival via binding to fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 (Fn14) and subsequent activation of the transcription factor NF-κB. To discover small molecule inhibitors that disrupt the TWEAK-Fn14 signaling axis, we utilized a cell-based drug-screening assay using HEK293 cells engineered to express both Fn14 and a NF-κB-driven firefly luciferase reporter protein. Focusing on the LOPAC1280 library of 1280 pharmacologically active compounds, we identified aurintricarboxylic acid (ATA) as an agent that suppressed TWEAK-Fn14-NF-κB dependent signaling, but not TNFα-TNFR-NF-κB driven signaling. We demonstrated that ATA repressed TWEAK-induced glioma cell chemotactic migration and invasion via inhibition of Rac1 activation but had no effect on cell viability or Fn14 expression. In addition, ATA treatment enhanced glioma cell sensitivity to both the chemotherapeutic agent temozolomide (TMZ) and radiation-induced cell death. In summary, this work reports a repurposed use of a small molecule inhibitor that targets the TWEAK-Fn14 signaling axis, which could potentially be developed as a new therapeutic agent for treatment of GBM patients.
Keywords: Fn14; aurintricarboxylic acid; glioblastoma; invasion; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The author's have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- Johnson DR, Galanis E. Medical management of high-grade astrocytoma: current and emerging therapies. Semin Oncol. 2014;41:511–522. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B, Belanger K, Hau P, Brandes AA, Gijtenbeek J, Marosi C, Vecht CJ, Mokhtari K, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:459–466. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–996. - PubMed
-
- Giese A, Bjerkvig R, Berens ME, Westphal M. Cost of migration: invasion of malignant gliomas and implications for treatment. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:1624–1636. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

