Prognostic and predictive value of VHL gene alteration in renal cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis and review
- PMID: 28103578
- PMCID: PMC5355155
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14704
Prognostic and predictive value of VHL gene alteration in renal cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis and review
Abstract
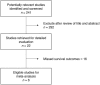
The von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) gene is often inactivated in sporadic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) by mutation or promoter hypermethylation. The prognostic or predictive value of VHL gene alteration is not well established. We conducted this meta-analysis to evaluate the association between the VHL alteration and clinical outcomes in patients with RCC. We searched PUBMED, MEDLINE and EMBASE for articles including following terms in their titles, abstracts, or keywords: 'kidney or renal', 'carcinoma or cancer or neoplasm or malignancy', 'von Hippel-Lindau or VHL', 'alteration or mutation or methylation', and 'prognostic or predictive'. There were six studies fulfilling inclusion criteria and a total of 633 patients with clear cell RCC were included in the study: 244 patients who received anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapy in the predictive value analysis and 419 in the prognostic value analysis. Out of 663 patients, 410 (61.8%) had VHL alteration. The meta-analysis showed no association between the VHL gene alteration and overall response rate (relative risk = 1.47 [95% CI, 0.81-2.67], P = 0.20) or progression free survival (hazard ratio = 1.02 [95% CI, 0.72-1.44], P = 0.91) in patients with RCC who received VEGF-targeted therapy. There was also no correlation between the VHL alteration and overall survival (HR = 0.80 [95% CI, 0.56-1.14], P = 0.21). In conclusion, this meta-analysis indicates that VHL gene alteration has no prognostic or predictive value in patients with clear cell RCC.
Keywords: anti-VEGF therapy; meta-analysis; prognosis; renal cell carcinoma; von Hippel-Lindau.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

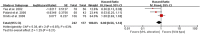
Similar articles
-
Clinicopathologic Significance of VHL Gene Alteration in Clear-Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: An Updated Meta-Analysis and Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 26;19(9):2529. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092529. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30149673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Somatic VHL alteration and its impact on prognosis in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2005 May;13(5):859-64. Oncol Rep. 2005. PMID: 15809750
-
Unique molecular alteration patterns in von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) gene in a cohort of sporadic renal cell carcinoma patients from Pakistan.Mutat Res. 2014 May-Jun;763-764:45-52. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2014.03.008. Epub 2014 Apr 12. Mutat Res. 2014. PMID: 24727139 Clinical Trial.
-
Prognostic Value of the VHL, HIF-1α, and VEGF Signaling Pathway and Associated MAPK (ERK1/2 and ERK5) Pathways in Clear-Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. A Long-Term Study.Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2017 Dec;15(6):e923-e933. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2017.05.016. Epub 2017 May 25. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28624320
-
VHL gene mutations in renal cell carcinoma: role as a biomarker of disease outcome and drug efficacy.Curr Oncol Rep. 2009 Mar;11(2):94-101. doi: 10.1007/s11912-009-0015-5. Curr Oncol Rep. 2009. PMID: 19216840 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The application of radiomics in predicting gene mutations in cancer.Eur Radiol. 2022 Jun;32(6):4014-4024. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08520-6. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35048135 Review.
-
Genomic profiling in renal cell carcinoma.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020 Aug;16(8):435-451. doi: 10.1038/s41581-020-0301-x. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32561872 Review.
-
Clinicopathological and Molecular Features of Secondary Cancer (Metastasis) to the Thyroid and Advances in Management.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 17;23(6):3242. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063242. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Overview of Systemic Targeted Therapy in Renal Cell Carcinoma, with a Focus on Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma and Brain Metastases.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Sep 21;45(9):7680-7704. doi: 10.3390/cimb45090485. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37754269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-angiogenesis and Immunotherapy: Novel Paradigms to Envision Tailored Approaches in Renal Cell-Carcinoma.J Clin Med. 2020 May 24;9(5):1594. doi: 10.3390/jcm9051594. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32456352 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Diaz JI, Mora LB, Hakam A. The Mainz Classification of Renal Cell Tumors. Cancer Control. 1999(6):571–9. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016(66):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Janzen NK, Kim HL, Figlin RA, Belldegrun AS. Surveillance after radical or partial nephrectomy for localized renal cell carcinoma and management of recurrent disease. Urol Clin North Am. 2003(30):843–52. - PubMed
-
- Richards FM. Molecular pathology of von HippelLindau disease and the VHL tumour suppressor gene. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2001(2001):1–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

