Significant efficacy and well safety of apatinib in an advanced liver cancer patient: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 28103584
- PMCID: PMC5386780
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14724
Significant efficacy and well safety of apatinib in an advanced liver cancer patient: a case report and literature review
Abstract
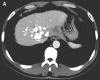
Apatinib is a novel and highly selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2. Previous studies have suggested that apatinib is safe and effective in some solid tumors. We report one case with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), who received apatinib combined with transhepatic arterial chemotherapy and embolization (TACE), and chemotherapy respectively. TACE was administered three times once a month, using lipiodol 10ml, oxaliplatin 150mg, and tegafur 1g. The dose of apatinib was 500 mg/d from day 4 to 24. After TACE, the patient received chemotherapy of regimen FOLFOX4, oxaliplatin intravenously at 85 mg/m2 on day 1, calcium levofolinate 200 mg/m2 on day 1 and 2, 5-fluorouracil 400 mg/m2 intravenously and 5-fluorouracil 600 mg/m2 intravenously pumped for 22h on day 1 and 2, cycled every two weeks for seven cycles. He took concurrently apatinib with a dose of 500mg daily from 1 to 10 days per cycle. He was confirmed as partial response (PR) by the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST). The level of serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) decreased from 60500 ng/ml to 12.7 ng/ml, and the progression free survival (PFS) time was more than eight months. It indicated that apatinib may be a superior choice for HCC patients.
Keywords: apatinib; hepatocellular carcinoma; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–32. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Qin S, Xu J, Guo W, Xiong J, Bai Y, Sun G, Yang Y, Wang L, Xu N, Cheng Y, Wang Z, Zheng L, et al. Apatinib for chemotherapy-refractory advanced metastatic gastric cancer: results from a randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-arm, phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3219–25. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Qin S, Xu J, Xiong J, Wu C, Bai Y, Liu W, Tong J, Liu Y, Xu R, Wang Z, Wang Q, Ouyang X, et al. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase III Trial of Apatinib in Patients With Chemotherapy-Refractory Advanced or Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach or Gastroesophageal Junction. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:1448–54. - PubMed
-
- Qin S. Apatinib in Chinese patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase II randomized, open-label trial. Journal Of Clinical Oncology. 2014;32(Suppl 5) abstract 4019.
-
- Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, Xu J, Sun Y, Liang H, et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:25–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

