Long-Term Exposure to Imatinib Mesylate Downregulates Hippo Pathway and Activates YAP in a Model of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
- PMID: 28103766
- PMCID: PMC5421616
- DOI: 10.1089/scd.2016.0262
Long-Term Exposure to Imatinib Mesylate Downregulates Hippo Pathway and Activates YAP in a Model of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
Abstract
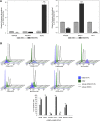
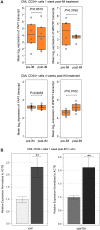
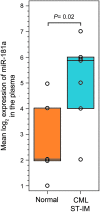
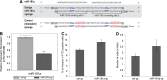
Despite the success of tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy in chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), leukemic stem/progenitor cells remain detectable even in the state of deep molecular remission. Mechanisms that allow them to persist despite continued kinase inhibition remain unclear. We have previously shown that prolonged exposure to imatinib mesylate (IM) results in dysregulation of Akt/Erk 1/2 signaling, upregulation of miR-181a, enhanced adhesiveness, and resistance to high IM. To characterize the molecular basis and reversibility of those effects, we applied gene and protein expression analysis, quantitative phosphoproteomics, and direct miR-181a inhibition to our cellular model of CML cells subjected to prolonged exposure to IM. Those cells demonstrated upregulation of pluripotency markers (SOX2, SALL4) and adhesion receptors (CD44, VLA-4, CXCR4), as well as downregulation of Hippo signaling and upregulation of transcription coactivator YAP. Furthermore, inhibition of miR-181a using a microRNA sponge inhibitor resulted in decreased transcription of SOX2 and SALL4, decreased activation of YAP, and increased sensitivity to IM. Our findings indicate that long-term exposure to IM results in dysregulation of stem cell renewal-regulatory Hippo/YAP signaling, acquisition of expression of stem cell markers and that experimental interference with YAP activity may help to restore chemosensitivity to TKI.
Keywords: Hippo pathway; YAP; chemoresistance; imatinib mesylate; leukemic stem cells; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Expression of Hippo signaling pathway and Aurora kinase genes in chronic myeloid leukemia.Med Oncol. 2018 Jan 31;35(3):26. doi: 10.1007/s12032-018-1079-6. Med Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29387948
-
Inhibition of YAP suppresses CML cell proliferation and enhances efficacy of imatinib in vitro and in vivo.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Sep 6;35(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0414-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27599610 Free PMC article.
-
EPS8 regulates proliferation, apoptosis and chemosensitivity in BCR-ABL positive cells via the BCR-ABL/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.Oncol Rep. 2018 Jan;39(1):119-128. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.6102. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29192326 Free PMC article.
-
[MET/ERK and MET/JNK Pathway Activation Is Involved in BCR-ABL Inhibitor-resistance in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018;138(12):1461-1466. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00142. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018. PMID: 30504658 Review. Japanese.
-
Hippo-yap signaling in ocular development and disease.Dev Dyn. 2018 Jun;247(6):794-806. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.24628. Epub 2018 Apr 23. Dev Dyn. 2018. PMID: 29532607 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Hippo-YAP signaling by insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in the tumorigenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Jun 16;13(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00906-1. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32546241 Free PMC article.
-
YAP/TAZ Signaling and Resistance to Cancer Therapy.Trends Cancer. 2019 May;5(5):283-296. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2019.02.010. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Trends Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31174841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-181a: regulatory roles, cancer-associated signaling pathway disruptions, and therapeutic potential.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2024 Dec;28(12):1061-1091. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2024.2433687. Epub 2024 Dec 8. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2024. PMID: 39648331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-181a plays the tumor-suppressor role in chronic myeloid leukemia CD34 + cells partially via SERPINE1.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Dec 16;81(1):10. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-05036-8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 38103082 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive phenotypic modulations lead to therapy resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia cells.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 27;15(2):e0229104. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229104. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32106243 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bower H, Bjorkholm M, Dickman PW, Hoglund M, Lambert PC. and Andersson TM. (2016). Life Expectancy of Patients With Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Approaches the Life Expectancy of the General Population. J Clin Oncol 34:2851–2857 - PubMed
-
- Rousselot P, Charbonnier A, Cony-Makhoul P, Agape P, Nicolini FE, Varet B, Gardembas M, Etienne G, Rea D, et al. (2014). Loss of major molecular response as a trigger for restarting tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in patients with chronic-phase chronic myelogenous leukemia who have stopped imatinib after durable undetectable disease. J Clin Oncol 32:424–430 - PubMed
-
- Chomel JC, Bonnet ML, Sorel N, Sloma I, Bennaceur-Griscelli A, Rea D, Legros L, Marfaing-Koka A, Bourhis JH, et al. (2016). Leukemic stem cell persistence in chronic myeloid leukemia patients in deep molecular response induced by tyrosine kinase inhibitors and the impact of therapy discontinuation. Oncotarget 7:35293–35301 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

