Demographics of patients receiving Intravitreal anti-VEGF treatment in real-world practice: healthcare research data versus randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 28103831
- PMCID: PMC5244516
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-017-0401-y
Demographics of patients receiving Intravitreal anti-VEGF treatment in real-world practice: healthcare research data versus randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: While randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are based on strict inclusion/exclusion criteria, non-interventional studies (NISs) might provide additional information to guide management in patients more representative to the real-world setting. The aim of this study was to compare baseline characteristics of patients receiving intravitreal treatment in the NIS OCEAN with those from published RCTs.
Methods: The ongoing OCEAN study enrolled patients treated with ranibizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD), diabetic macular oedema (DME) or branch/central retinal vein occlusion (B/CRVO). Baseline patient characteristics were compared by indication within the OCEAN cohort. Furthermore, the characteristics were set in reference to those of published RCTs in the same indications. Confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated and assessed for statistically significant differences as indicated by non-overlapping CIs.
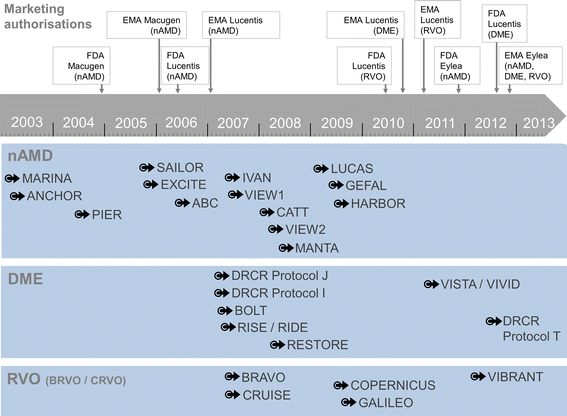
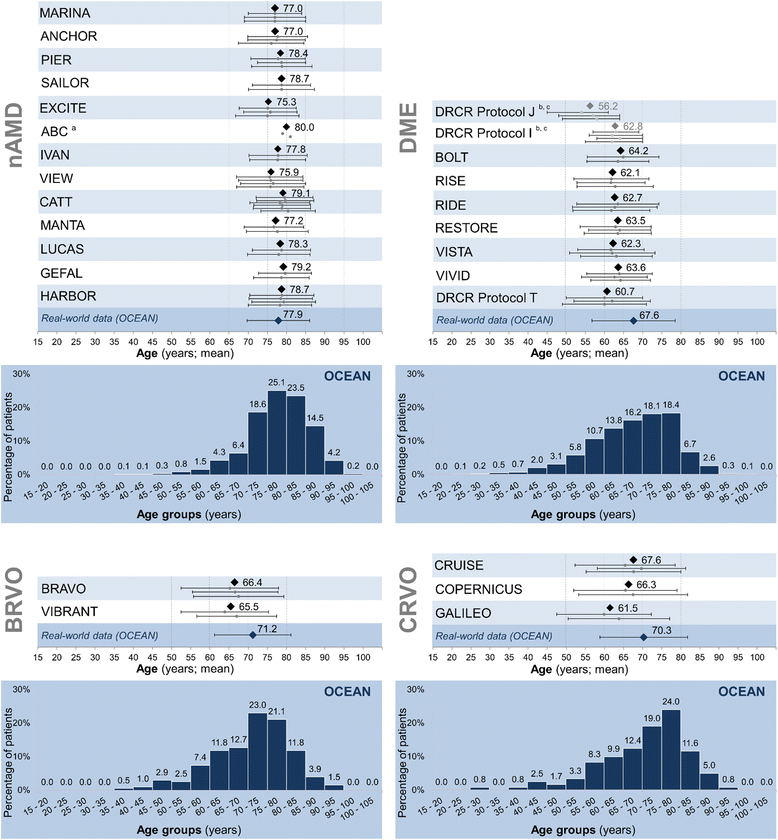
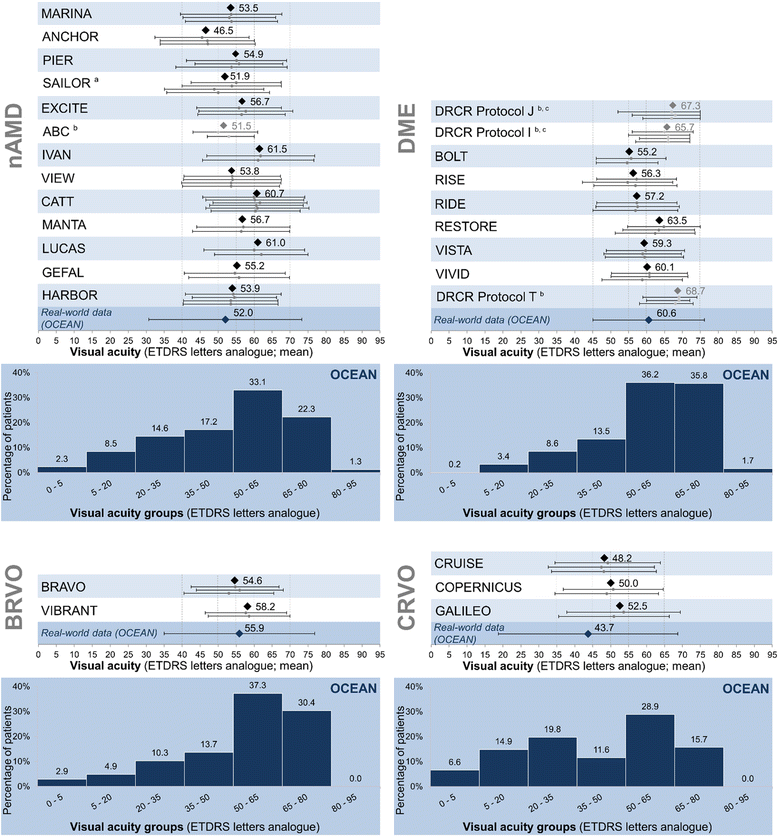
Results: Patient characteristics in the NIS OCEAN were evaluated for 3,614 patients with nAMD, 1,211 with DME, 204 with BRVO and 121 with CRVO. Between these groups, significant differences in mean age, gender distributions, and mean baseline VA were seen, reflecting known differences between the indications. Compared to the patient characteristics of published RCTs (trials selected by literature search: nAMD: 13 RCTs, DME: 9, RVO: 5), the OCEAN patients' mean age was significantly higher in every indication. The gender distributions across the trials were comparable, with only few differences between OCEAN and the RCTs. Regarding the mean baseline VA, notable differences were found in nAMD and in DME, with VA significantly higher in some RCTs and lower in others.
Conclusions: The described differences underline the complementarity of NISs and RCTs. OCEAN covers a broader spectrum and more variability of patients than do RCTs. As baseline values may have impact on the treatment response (ceiling effect), there is an ongoing need for research in all patient subgroups. Country-specific assessments of patient populations can better reflect the real-world situation. NISs can deliver insights that RCTs may not, as NISs can include non-typical patients, patients with comorbidities, a broader age spectrum and patients of various disease stages.
Trial registration: The NIS OCEAN was registered on www.clinicaltrials.gov (identifier: NCT02194803 ).
Keywords: Anti-VEGF; Ceiling effect; DME; Demographic characteristics; Epidemiology; NAMD; Non-interventional study; RVO.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

