Discovery and validation of immune-associated long non-coding RNA biomarkers associated with clinically molecular subtype and prognosis in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- PMID: 28103885
- PMCID: PMC5248456
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-017-0580-4
Discovery and validation of immune-associated long non-coding RNA biomarkers associated with clinically molecular subtype and prognosis in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Abstract
Background: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is an aggressive and complex disease characterized by wide clinical, phenotypic and molecular heterogeneities. The expression pattern and clinical implication of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) between germinal center B-cell-like (GCB) and activated B-cell-like (ABC) subtypes in DLBCL remain unclear. This study aims to determine whether lncRNA can serve as predictive biomarkers for subtype classification and prognosis in DLBCL.
Methods: Genome-wide comparative analysis of lncRNA expression profiles were performed in a large number of DLBCL patients from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO), including GSE31312 cohort (N = 426), GSE10846 (N = 350) cohort and GSE4475 cohort (N = 129). Novel lncRNA biomarkers associated with clinically molecular subtype and prognosis were identified in the discovery cohort using differential expression analyses and weighted voting algorithm. The predictive value of the lncRNA signature was then assessed in two independent cohorts. The functional implication of lncRNA signature was also analyzed by integrative analysis of lncRNA and mRNA.
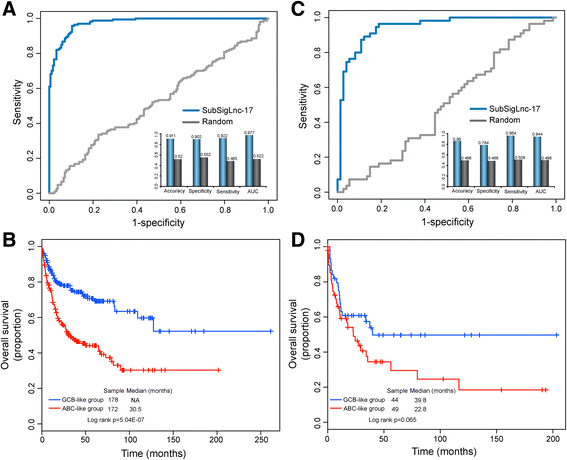
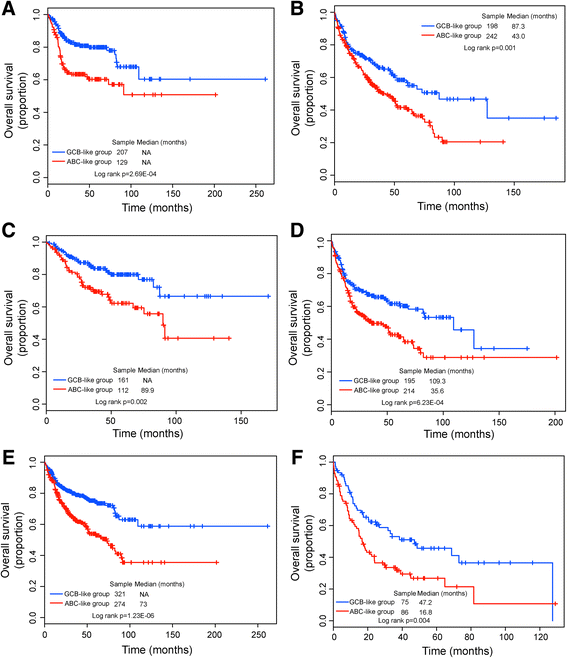
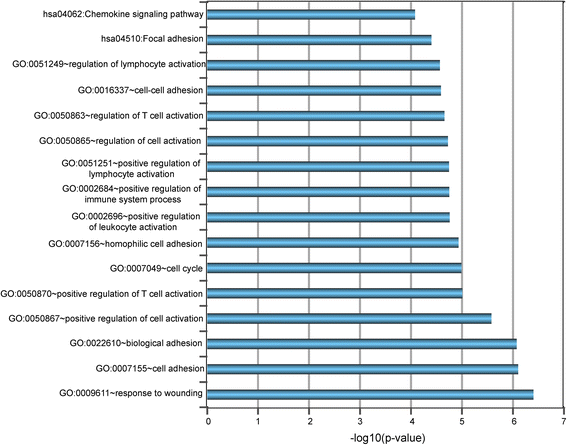
Results: Seventeen of the 156 differentially expressed lncRNAs between GCB and ABC subtypes were identified as candidate biomarkers and integrated into form a lncRNA-based signature (termed SubSigLnc-17) which was able to discriminate between GCB and ABC subtypes with AUC of 0.974, specificity of 89.6% and sensitivity of 92.5%. Furthermore, subgroups of patients characterized by the SubSigLnc-17 demonstrated significantly different clinical outcome. The reproducible predictive power of SubSigLnc-17 in subtype classification and prognosis was successfully validated in the internal validation cohort and another two independent patient cohorts. Integrative analysis of lncRNA-mRNA suggested that these candidate lncRNA biomarkers were mainly related to immune-associated processes, such as T cell activation, leukocyte activation, lymphocyte activation and Chemokine signaling pathway.
Conclusions: Our study uncovered differentiated lncRNA expression pattern between GCB and ABC DLBCL and identified a 17-lncRNA signature for subtype classification and prognosis prediction. With further prospective validation, our study will improve the understanding of underlying molecular heterogeneities in DLBCL and provide candidate lncRNA biomarkers in DLBCL classification and prognosis.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; Long non-coding RNAs; Prognosis; Subtype classification.
Figures



References
-
- Tilly H, Gomes da Silva M, Vitolo U, Jack A, Meignan M, Lopez-Guillermo A, Walewski J, Andre M, Johnson PW, Pfreundschuh M, et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(Suppl 5):v116–125. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv304. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

