T-cadherin deficiency increases vascular vulnerability in T2DM through impaired NO bioactivity
- PMID: 28103886
- PMCID: PMC5244578
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-016-0488-0
T-cadherin deficiency increases vascular vulnerability in T2DM through impaired NO bioactivity
Abstract
Background: Endothelial dysfunction plays a critical role in the development of type 2 diabetes (T2DM). T-cadherin (T-cad) has gained recognition as a regulator of endothelial cell (EC) function. The present study examined whether T-cad deficiency increases vascular vulnerability in T2DM.
Methods: Vascular segments were isolated from WT or T-cad knockout mice. Endothelial function, total NO accumulation, and the expression of T-cad related proteins were determined.
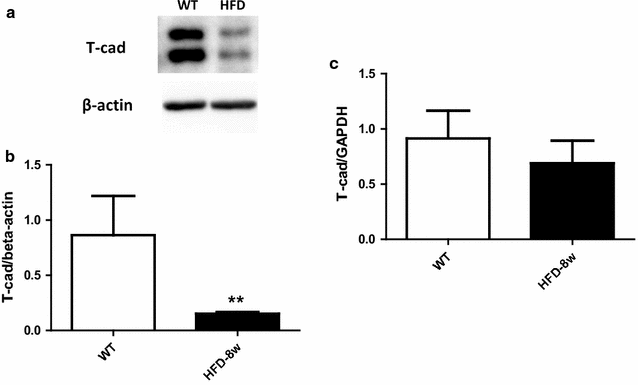
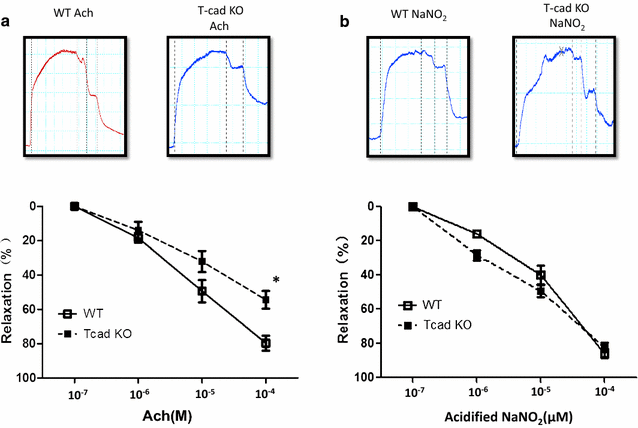
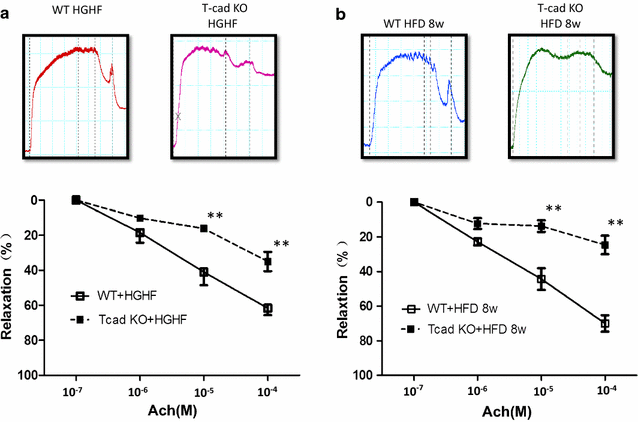
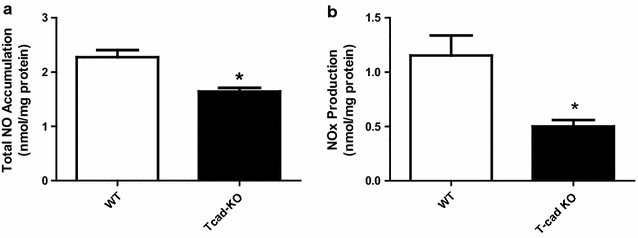
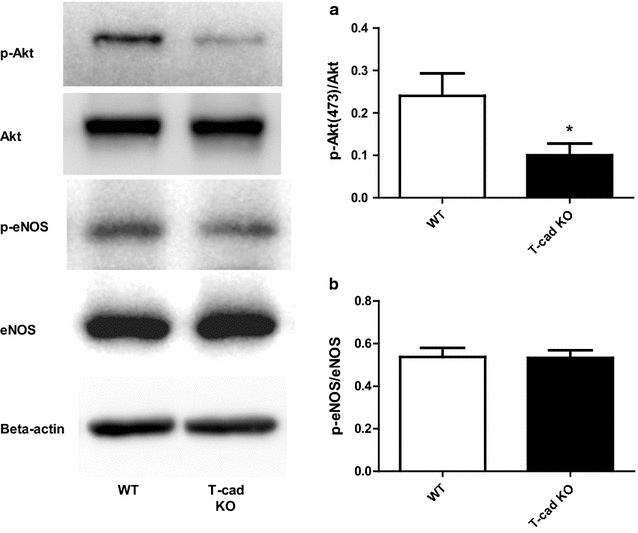
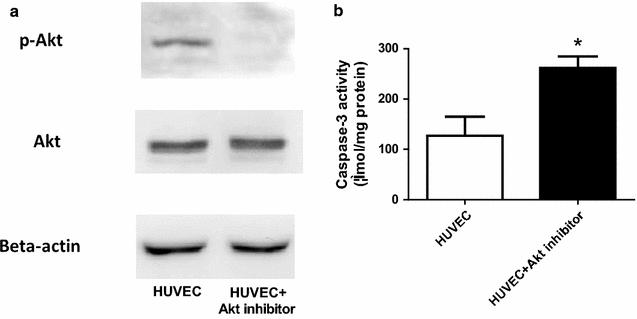
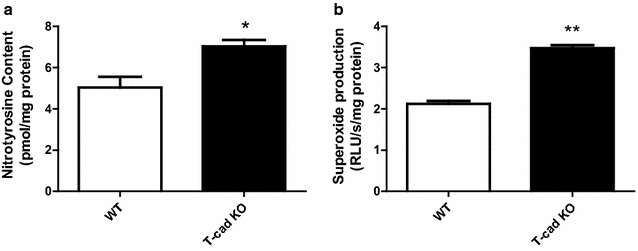
Results: Ach and acidified NaNO2 induced similar vasorelaxation in WT groups. T-cad KO mice exhibited normal response to acidified NaNO2, but manifested markedly reduced response to Ach. NO accumulation was also decreased in T-cad KO group. T-cad expression was reduced in WT mice fed 8 weeks of high fat diet (HFD). Furthermore, exacerbated reduction of vasorelaxation was observed in T-cad KO mice fed 8 weeks of HFD.
Conclusions: In the current study, we provide the first in vivo evidence that T-cadherin deficiency causes endothelial dysfunction in T2DM vascular segments, suggesting the involvement of T-cad deficiency in T2DM pathogenesis.
Keywords: Endothelial cell; Endothelial dysfunction; NO bioactivity; T-cadherin; T2DM; Vascular ring.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Galectin-3 deficiency exacerbates hyperglycemia and the endothelial response to diabetes.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015 Jun 6;14:73. doi: 10.1186/s12933-015-0230-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015. PMID: 26047815 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-linolenic acid intake prevents endothelial dysfunction in high-fat diet-fed streptozotocin rats and underlying mechanisms.Vasa. 2013 Nov;42(6):421-8. doi: 10.1024/0301-1526/a000311. Vasa. 2013. PMID: 24220118
-
Low dose dietary nitrate improves endothelial dysfunction and plaque stability in the ApoE-/- mouse fed a high fat diet.Free Radic Biol Med. 2016 Oct;99:189-198. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.08.009. Epub 2016 Aug 9. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27519268
-
Uncoupling protein-2 protects endothelial function in diet-induced obese mice.Circ Res. 2012 Apr 27;110(9):1211-6. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.262170. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22461387
-
NO-dependent endothelial dysfunction in type II diabetes is aggravated by dyslipidemia and hypertension, but can be restored by angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and weight loss.J Vasc Res. 2013;50(6):486-97. doi: 10.1159/000355221. Epub 2013 Oct 31. J Vasc Res. 2013. PMID: 24192582
Cited by
-
New evidence for T-cadherin in COVID-19 pathogenesis, endothelial dysfunction, and lung fibrosis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Mar 5;13:1476329. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1476329. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40109358 Free PMC article.
-
T-Cadherin Deficiency Is Associated with Increased Blood Pressure after Physical Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 17;24(18):14204. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814204. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762507 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the enigmatic role of T-cadherin in tumor angiogenesis.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 31;16:1564130. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1564130. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40230838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of adiponectin in osteoarthritis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 8;10:992764. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.992764. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36158216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial dysfunction and platelet hyperactivity in type 2 diabetes mellitus: molecular insights and therapeutic strategies.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018 Aug 31;17(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12933-018-0763-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018. PMID: 30170601 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pieper GM, Meier DA, Hager SR. Endothelial dysfunction in a model of hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia. Am J Physiol. 1995;269(3 Pt 2):H845–H850. - PubMed
-
- Bohlen HG, Lash JM. Topical hyperglycemia rapidly suppresses EDRF-mediated vasodilation of normal rat arterioles. Am J Physiol. 1993;265(1 Pt 2):H219–H225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

