Inhibition of P-glycoprotein, multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 and cytochrome P450 3A4 improves the oral absorption of octreotide in rats with portal hypertension
- PMID: 28105103
- PMCID: PMC5228395
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2016.3808
Inhibition of P-glycoprotein, multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 and cytochrome P450 3A4 improves the oral absorption of octreotide in rats with portal hypertension
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Inhibition of P-glycoprotein, multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 and cytochrome P450 3A4 improves the oral absorption of octreotide in rats with portal hypertension.Exp Ther Med. 2022 May;23(5):354. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11281. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35481223 Free PMC article.
Abstract
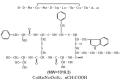
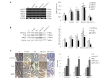
The aim of the present study was to increase the intestinal transport of octreotide (OCT) by targeting the first-pass impact to identify a potential method for decreasing portal vein pressure (PVP) using oral OCT. Thus, the bioavailability of intestinally absorbed OCT was evaluated in normal rats and rats with portal hypertension (PH) that had been administered P-glycoprotein/multidrug resistance-associated protein 2/cytochrome P450 3A4 (P-gp/MRP2/CYP3A4) inhibitors. The mRNA and protein expression levels of P-gp, MRP2 and CYP3A4 were evaluated in normal and PH rats with or without OCT and the inhibitors using RT-PCR, western blot and immunohistochemical analyses. The potential effects of the inhibitor administration on PVP were also examined. The results suggest that P-gp, MRP2 and CYP3A4 play important roles in prohibiting the enteral absorption of OCT, particularly under a PH environment. Moreover, inhibitors of P-gp, MRP2 and CYP3A4 decrease the first-pass effects of OCT and effectively reduce PVP under PH conditions. Therefore, the present results suggest P-gp, MRP2 and CYP3A4 are key factors in the intestinal absorption of OCT. The inhibition of P-gp, MRP2 and CYP3A4 can markedly decrease the first-pass effects of OCT, and their use may facilitate the use of orally administered OCT.
Keywords: P-glycoprotein; absorption; cytochrome P450 3A4; multidrug resistance-associated protein 2; octreotide.
Figures
References
-
- Spahr L, Giostra E, Frossard JL, Morard I, Mentha G, Hadengue A. A 3-month course of long-acting repeatable octreotide (sandostatin LAR) improves portal hypertension inpatients with cirrhosis: A randomized controlled study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:1397–1405. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01262.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Biron E, Chatterjee J, Ovadia O, Langenegger D, Brueggen J, Hoyer D, Schmid HA, Jelinek R, Gilon C, Hoffman A, Kessler H. Improving oral bioavailability of peptides by multiple N-methylation: Somatostatin analogues. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2008;47:2595–2599. doi: 10.1002/anie.200705797. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Thanou M, Verhoef JC, Marbach P, Junginger HE. Intestinal absorption of octreotide: N-trimethyl chitosan chloride (TMC) ameliorates the permeability and absorption properties of the somatostatin analogue in vitro and in vivo. J Pharm Sci. 2000;89:951–957. doi: 10.1002/1520-6017(200007)89:7<951::AID-JPS13>3.0.CO;2-1. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
