Acellular Dermal Matrix (Permacol®) for Heterologous Immediate Breast Reconstruction after Skin-Sparing Mastectomy in Patients with Breast Cancer: A Single-Institution Experience and a Review of the Literature
- PMID: 28105410
- PMCID: PMC5213735
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2016.00072
Acellular Dermal Matrix (Permacol®) for Heterologous Immediate Breast Reconstruction after Skin-Sparing Mastectomy in Patients with Breast Cancer: A Single-Institution Experience and a Review of the Literature
Abstract
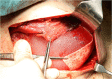
Objective: Skin-sparing mastectomy (SSM) with immediate heterologous reconstruction is a safe oncological option in surgical therapy of early breast cancer. Permacol® is an acellular dermal matrix (ADM) placed between the implant and the skin to improve lower pole projection and implant coverage. The aim of our study was to evaluate the outcome with a focus on patient satisfaction after 6 months and to analyze physical changes of ADM.
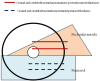
Methods: 10 patients who underwent SSM with Permacol® were analyzed retrospectively. All patients were followed using a satisfaction questionnaire and an ultrasound evaluation of the tissue thickness of the pectoralis muscle and the Permacol®.
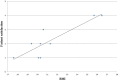
Results: No intraoperative complications were observed. One patient required removal of the implant for necrosis after 3 months. Half of the patients underwent secondary corrective surgery. A statistically significant thinning of the pectoralis muscle was observed, compared to the thickening of the Permacol®. A majority of the patients were satisfied with the operation, and we found a correlation between lower body mass index and patient satisfaction.
Conclusion: In our small case series Permacol®-assisted immediate reconstruction is shown to be an option for selected cases. Physical changes of Permacol® result in a symmetrical coverage of the implant, which may improve cosmetic outcome.
Keywords: Permacol®; acellular dermal matrices; breast cancer; heterologous immediate breast reconstruction; skin-sparing mastectomy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prepectoral implant placement and complete coverage with porcine acellular dermal matrix: a new technique for direct-to-implant breast reconstruction after nipple-sparing mastectomy.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2015 Feb;68(2):162-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2014.10.012. Epub 2014 Oct 16. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2015. PMID: 25455288
-
Comparative Study of Nipple-Areola Complex Position and Patient Satisfaction After Unilateral Mastectomy and Immediate Expander-Implant Reconstruction Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy Versus Skin-Sparing Mastectomy.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2019 Apr;43(2):313-327. doi: 10.1007/s00266-018-1217-8. Epub 2019 Feb 11. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2019. PMID: 30746565
-
Quality of life and patient satisfaction after one-stage implant-based breast reconstruction with an acellular dermal matrix versus two-stage breast reconstruction (BRIOS): primary outcome of a randomised, controlled trial.Lancet Oncol. 2018 Sep;19(9):1205-1214. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30378-4. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Lancet Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30104147 Clinical Trial.
-
The evolving role of pre-pectoral ADM-assisted implant-based immediate breast reconstruction following skin-sparing mastectomy.Am J Surg. 2018 Sep;216(3):639-640. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2018.01.021. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Am J Surg. 2018. PMID: 29397895 Review.
-
The cost effectiveness of acellular dermal matrix in expander-implant immediate breast reconstruction.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2014 Apr;67(4):468-76. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2013.12.035. Epub 2014 Jan 23. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2014. PMID: 24508194 Review.
Cited by
-
Decellularized Extracellular Matrix Scaffolds for Soft Tissue Augmentation: From Host-Scaffold Interactions to Bottlenecks in Clinical Translation.Biomater Res. 2024 Sep 6;28:0071. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0071. eCollection 2024. Biomater Res. 2024. PMID: 39247652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical applications of acellular dermal matrices: A review.Scars Burn Heal. 2022 Jan 19;8:20595131211038313. doi: 10.1177/20595131211038313. eCollection 2022 Jan-Dec. Scars Burn Heal. 2022. PMID: 35083065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breast Reconstruction after Mastectomy with the Use of an Implant and Serratus Anterior Fascia Flap-Initial Clinical Evaluation.J Pers Med. 2021 Nov 3;11(11):1142. doi: 10.3390/jpm11111142. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34834494 Free PMC article.
-
Submuscular and Pre-Pectoral ADM Assisted Immediate Breast Reconstruction: A Literature Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 May 26;56(6):256. doi: 10.3390/medicina56060256. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020. PMID: 32466619 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bundesamt für Statistik. Neuchâtel. Neuchâtel: Bundesamt für Statistik; (2015).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources