Subureteral Injection with Small-Size Dextranomer/Hyaluronic Acid Copolymer: Is It Really Efficient?
- PMID: 28105412
- PMCID: PMC5220383
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/2168753
Subureteral Injection with Small-Size Dextranomer/Hyaluronic Acid Copolymer: Is It Really Efficient?
Abstract
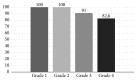
The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical results of patients with vesicoureteral reflux, which were treated with subureteral injection of small-size (80-120 μm) dextranomer/hyaluronic acid copolymer (Dx/HA). Data of 75 children (105 renal units) who underwent STING procedure with small-size Dx/HA for the treatment of vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) in our clinic between 2008 and 2012 were retrospectively analyzed. Preoperative reflux grade and side, injection indication, postoperative urinary infections and urinary symptoms, voiding cystourethrogram, and renal scintigraphy results were evaluated. The success rate of the procedure was 100% in patients with grades 1 and 2 reflux, 91% in patients with grade 3 reflux, and 82.6% in patients with grade 4. Overall success rate of the treated patients was 97%. Endoscopic subureteric injection with Dx/HA procedure has become a reasonable minimally invasive alternative technique to open surgery, long-term antibiotic prophylaxis, and surveillance modalities in treatment of VUR in terms of easy application, low costs and complication rates, and high success rates. Injection material composed of small-size dextranomer microspheres seems superior to normal size Dx/HA, together with offering similar success with low cost.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Comment on "Subureteral Injection with Small-Size Dextranomer/Hyaluronic Acid Copolymer: Is It Really Efficient?".Biomed Res Int. 2018 Aug 12;2018:4078183. doi: 10.1155/2018/4078183. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30159327 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Surgical Outcome Analysis of Pneumovesicoscopic Ureteral Reimplantation and Endoscopic Dextranomer/Hyaluronic Acid Injection for Primary Vesicoureteral Reflux in Children: A Multicenter 12-Year Review.J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2018 Mar;28(3):348-353. doi: 10.1089/lap.2017.0281. Epub 2017 Dec 22. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2018. PMID: 29271690
-
Factors affecting the success of endoscopic treatment of vesicoureteral reflux and comparison of two dextranomer based bulking agents: does bulking substance matter?J Pediatr Urol. 2015 Apr;11(2):90.e1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2014.12.009. Epub 2015 Mar 2. J Pediatr Urol. 2015. PMID: 25791422
-
Febrile urinary tract infections after ureteroneocystostomy and subureteral injection of dextranomer/hyaluronic acid for vesicoureteral reflux--do choice of procedure and success matter?J Urol. 2013 Jan;189(1):275-82. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.09.011. Epub 2012 Nov 20. J Urol. 2013. PMID: 23174239
-
Part 3: Endoscopic injection versus antibiotic prophylaxis in the reduction of urinary tract infections in patients with vesicoureteral reflux.Curr Med Res Opin. 2007 Sep;23 Suppl 4:S15-20. doi: 10.1185/030079907X226230. Curr Med Res Opin. 2007. PMID: 17931480 Review.
-
Endoscopic treatment of vesicoureteral reflux using dextranomer hyaluronic acid copolymer.J Pediatr Urol. 2008 Jun;4(3):221-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2007.11.015. Epub 2008 Mar 5. J Pediatr Urol. 2008. PMID: 18631931 Review.
Cited by
-
Management of Vesicoureteral Reflux: What Have We Learned Over the Last 20 Years?Front Pediatr. 2021 Mar 31;9:650326. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.650326. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33869117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Examination of Complementary Medicine for Treating Urinary Tract Infections Among Pregnant Women and Children.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 27;13:883216. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.883216. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35571128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comment on "Subureteral Injection with Small-Size Dextranomer/Hyaluronic Acid Copolymer: Is It Really Efficient?".Biomed Res Int. 2018 Aug 12;2018:4078183. doi: 10.1155/2018/4078183. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30159327 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Sorensen M. D., Koyle M. A., Cowan C. A., Zamilpa I., Shnorhavorian M., Lendvay T. S. Injection volumes of dextranomer/hyaluronic acid are increasing in the endoscopic management of vesicoureteral reflux. Pediatric Surgery International. 2010;26(5):509–513. doi: 10.1007/s00383-010-2558-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Puri P., Kutasy B., Colhoun E., Hunziker M. Single center experience with endoscopic subureteral dextranomer/hyaluronic acid injection as first line treatment in 1,551 children with intermediate and high grade vesicoureteral reflux. Journal of Urology. 2012;188, supplement 4:1485–1489. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.02.023. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials