Dynamical states, possibilities and propagation of stress signal
- PMID: 28106087
- PMCID: PMC5247771
- DOI: 10.1038/srep40596
Dynamical states, possibilities and propagation of stress signal
Abstract
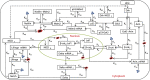
The stress driven dynamics of Notch-Wnt-p53 cross-talk is subjected to a few possible dynamical states governed by simple fractal rules, and allowed to decide its own fate by choosing one of these states which are contributed from long range correlation with varied fluctuations due to active molecular interaction. The topological properties of the networks corresponding to these dynamical states have hierarchical features with assortive structure. The stress signal driven by nutlin and modulated by mediator GSK3 acts as anti-apoptotic signal in this system, whereas, the stress signal driven by Axin and modulated by GSK3 behaves as anti-apoptotic for a certain range of Axin and GSK3 interaction, and beyond which the signal acts as favor-apoptotic signal. However, this stress system prefers to stay in an active dynamical state whose counterpart complex network is closest to hierarchical topology with exhibited roles of few interacting hubs. During the propagation of stress signal, the system allows the propagator pathway to inherit all possible properties of the state to the receiver pathway/pathways with slight modifications, indicating efficient information processing and democratic sharing of responsibilities in the system via cross-talk. The increase in the number of cross-talk pathways in the system favors to establish self-organization.
Figures
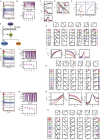
 vs q and Dq vs q, (D) Ap53 as a function of k35 for various values of k39:…., (E) phase diagram in the parameter space (
vs q and Dq vs q, (D) Ap53 as a function of k35 for various values of k39:…., (E) phase diagram in the parameter space ( ), where
), where  are the values of k35 cut by horizontal line, and Δk35 is the range of k35 occupied by sustain oscillation, (F) schematic diagram of stress signal propagation, (G) topological properties of networks constructed from the time series of corresponding dynamical states: P(k), C(k), Cn(k), CB(k), CC(k) and CE(k) as a function of degree k, (H) the propagated signal received by Notch and corresponding dynamical states, (I) permutation entropy (HNotch) calculation of the dynamical states, (J) Multifractal measures of dynamical states of Notch: plots of Fs vs s,
are the values of k35 cut by horizontal line, and Δk35 is the range of k35 occupied by sustain oscillation, (F) schematic diagram of stress signal propagation, (G) topological properties of networks constructed from the time series of corresponding dynamical states: P(k), C(k), Cn(k), CB(k), CC(k) and CE(k) as a function of degree k, (H) the propagated signal received by Notch and corresponding dynamical states, (I) permutation entropy (HNotch) calculation of the dynamical states, (J) Multifractal measures of dynamical states of Notch: plots of Fs vs s,  vs q and Dq vs q, (K) topological properties of the corresponding dynamical states: P(k), C(k), Cn(k), CB(k), CC(k) and CE(k) as a function of degree k, (L) dynamical states of Axin due to propagated signal, and (M) corresponding permutation entropy (HAxin) values, (N) Multifractal calculations, (O) topological properties of the networks constructed from the Axin dynamical states.
vs q and Dq vs q, (K) topological properties of the corresponding dynamical states: P(k), C(k), Cn(k), CB(k), CC(k) and CE(k) as a function of degree k, (L) dynamical states of Axin due to propagated signal, and (M) corresponding permutation entropy (HAxin) values, (N) Multifractal calculations, (O) topological properties of the networks constructed from the Axin dynamical states.
 vs q and Dq vs q, (D) Ap53 as a function of k22 for various values of k39:…., (E) phase diagram in the parameter space (
vs q and Dq vs q, (D) Ap53 as a function of k22 for various values of k39:…., (E) phase diagram in the parameter space ( ), and Δk22 is the range of k22 occupied by sustain oscillation, (F) schematic diagram of stress signal propagation, (G) topological properties of networks of corresponding dynamical states: P(k), C(k), Cn(k), CB(k), CC(k) and CE(k) as a function of degree k, (H) the propagated signal receied by Notch and corresponding dynamical states, (I) permutation entropy (HNotch) calculations, (J) Multifractal measures, (K) topological properties of the corresponding dynamical states.
), and Δk22 is the range of k22 occupied by sustain oscillation, (F) schematic diagram of stress signal propagation, (G) topological properties of networks of corresponding dynamical states: P(k), C(k), Cn(k), CB(k), CC(k) and CE(k) as a function of degree k, (H) the propagated signal receied by Notch and corresponding dynamical states, (I) permutation entropy (HNotch) calculations, (J) Multifractal measures, (K) topological properties of the corresponding dynamical states.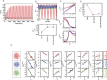
Similar articles
-
Dynamics of p53 and Wnt cross talk.Comput Biol Chem. 2015 Dec;59 Pt B:55-66. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2015.07.014. Epub 2015 Aug 23. Comput Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26375870
-
Control of apoptosis by SMAR1.Mol Biosyst. 2017 Jan 31;13(2):350-362. doi: 10.1039/c6mb00525j. Mol Biosyst. 2017. PMID: 27934984
-
Apoptosis regulatory protein-protein interaction demonstrates hierarchical scale-free fractal network.Brief Bioinform. 2015 Jul;16(4):675-99. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbu036. Epub 2014 Sep 24. Brief Bioinform. 2015. PMID: 25256288
-
The paradoxical pro- and anti-apoptotic actions of GSK3 in the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis signaling pathways.Prog Neurobiol. 2006 Jul;79(4):173-89. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2006.07.006. Epub 2006 Aug 28. Prog Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 16935409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics of p53: A Master Decider of Cell Fate.Genes (Basel). 2017 Feb 9;8(2):66. doi: 10.3390/genes8020066. Genes (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28208785 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring novel key regulators in breast cancer network.PLoS One. 2018 Jun 21;13(6):e0198525. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198525. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29927945 Free PMC article.
-
Transition and identification of pathological states in p53 dynamics for therapeutic intervention.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 27;11(1):2349. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82054-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33504910 Free PMC article.
-
Methodology of predicting novel key regulators in ovarian cancer network: a network theoretical approach.BMC Cancer. 2019 Nov 21;19(1):1129. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6309-6. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31752757 Free PMC article.
-
A Bioinformatics Approach to Identifying Potential Biomarkers for Cryptosporidium parvum: A Coccidian Parasite Associated with Fetal Diarrhea.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Dec 2;9(12):1427. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9121427. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34960172 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Phytonutrient Kaempferol in the Prevention of Gastrointestinal Cancers: Recent Trends and Future Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 27;16(9):1711. doi: 10.3390/cancers16091711. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38730663 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Heylighen F. The science of self-organization and adaptivity. The encyclopedia of life support systems. 5, 253–280 (2001).
-
- Prigogine I. & Stengers I. Order out of Chaos: Man’s New Dialogue with Nature (ed. Alvin T.) 1–349 (Bantam Books, 1984).
-
- Ashby W. R. Design for a Brain–The Origin of Adaptive Behavior (ed. Ashby W. R.) 1–304 (Chapman and Hall, London, 1952).
-
- Holland J. H. Hidden Order: How adaptation builds complexity (ed. Simmanons L. M.) 1–208 (Basic book, 1996).
-
- Holland J. H. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems: An Introductory Analysis with Applications to Biology. 1–227 (Control and Artificial Intelligence, MIT Press, Cambridge MA, 1992).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

