A drive in SUVs: From development to disease
- PMID: 28106510
- PMCID: PMC5406210
- DOI: 10.1080/15592294.2017.1281502
A drive in SUVs: From development to disease
Abstract
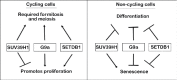
Progression of cells through distinct phases of the cell cycle, and transition into out-of-cycling states, such as terminal differentiation and senescence, is accompanied by specific patterns of gene expression. These cell fate decisions are mediated not only by distinct transcription factors, but also chromatin modifiers that establish heritable epigenetic patterns. Lysine methyltransferases (KMTs) that mediate methylation marks on histone and non-histone proteins are now recognized as important regulators of gene expression in cycling and non-cycling cells. Among these, the SUV39 sub-family of KMTs, which includes SUV39H1, SUV39H2, G9a, GLP, SETDB1, and SETDB2, play a prominent role. In this review, we discuss their biochemical properties, sub-cellular localization and function in cell cycle, differentiation programs, and cellular senescence. We also discuss their aberrant expression in cancers, which exhibit de-regulation of cell cycle and differentiation.
Keywords: Cancer; cell cycle; chromatin modifiers; differentiation; gene regulation; heterochromatin; histones; methylation.
Figures

References
-
- Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T. Regulation of chromatin by histone modifications. Cell Res 2011; 21:381-95; PMID:21321607; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/cr.2011.22 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Greer EL, Shi Y. Histone methylation: a dynamic mark in health, disease and inheritance. Nat Rev Genet 2012; 13:343-57; PMID:22473383; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nrg3173 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Reinberg D. Transcription regulation by histone methylation: interplay between different covalent modifications of the core histone tails. Genes Dev 2001; 15:2343-60; PMID:11562345; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1101/gad.927301 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jenuwein T, Laible G, Dorn R, Reuter G. SET domain proteins modulate chromatin domains in eu- and heterochromatin. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS 1998; 54:80-93; PMID:9487389; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1007/s000180050127 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
