NASPGHAN Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: Recommendations from the Expert Committee on NAFLD (ECON) and the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (NASPGHAN)
- PMID: 28107283
- PMCID: PMC5413933
- DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001482
NASPGHAN Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: Recommendations from the Expert Committee on NAFLD (ECON) and the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (NASPGHAN)
Abstract
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a highly prevalent chronic liver disease that occurs in the setting of insulin resistance and increased adiposity. It has rapidly evolved into the most common liver disease seen in the pediatric population and is a management challenge for general pediatric practitioners, subspecialists, and for health systems. In this guideline, the expert committee on NAFLD reviewed and summarized the available literature, formulating recommendations to guide screening and clinical care of children with NAFLD.
Conflict of interest statement
MV has research funding from Resonance Health Inc, serves on a DSMB for Aegerion and as a consultant for Shire, Immuron, Intercept and Target Pharmasolutions. SD serves on a DMC for Novo Nordisk and consults for Sanofi. RK has research funding from Raptor. The remaining authors have no personal or financial conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
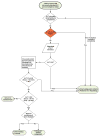
Screening labs: CBC with differential, AST, bilirubin (total, conjugated), alkaline phosphatase, GGT, INR, albumin, total protein, hemoglobin A1c
Exclude infections (e.g. hepatitis A IgM, hepatitis B surface antigen, hepatitis C antibody, other chronic viral infections)
Exclude endocrine disorders (TSH, free T4)
Exclude autoimmune causes of ALT elevation (total IgA, total IgG and tissue transglutaminase antibody, anti-nuclear antibody, anti-smooth muscle antibody, anti-liver kidney microsomal antibody)
Exclude genetic causes of ALT (ceruloplasmin and/or 24 hour urine copper, lysosomal acid lipase, alpha-1 antitrypsin phenotype)
Imaging: Abdominal ultrasound to rule out anatomical abnormalities or assess features of portal hypertension, magnetic resonance imaging or spectroscopy to measure hepatic fat.
Liver biopsy (histology, copper measurement, stain for microvesicular fat, assess fibrosis)

Comment in
-
Response to the Letters Regarding the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition NAFLD Guidelines.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017 Nov;65(5):e115-e116. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001731. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017. PMID: 29059122 No abstract available.
-
Please Do Not Forget Muscle Disease When Evaluating Elevated Transaminases.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017 Nov;65(5):e114. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001669. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017. PMID: 29064930 No abstract available.
-
Screening for NAFLD in Children: Do We Know the Optimal ALT Cut-off?J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017 Nov;65(5):e115. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001667. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017. PMID: 29064932 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wong RJ, Aguilar M, Cheung R, Perumpail RB, Harrison SA, Younossi ZM, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the second leading etiology of liver disease among adults awaiting liver transplantation in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2015;148(3):547–55. - PubMed
-
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Diehl AM, Brunt EM, Cusi K, et al. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatology. 2012;55(6):2005–23. - PubMed
-
- Vajro P, Lenta S, Socha P, Dhawan A, McKiernan P, Baumann U, et al. Diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents: position paper of the ESPGHAN Hepatology Committee. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012;54(5):700–13. - PubMed
-
- Louthan MV, Theriot JA, Zimmerman E, Stutts JT, McClain CJ. Decreased prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in black obese children. Journal of pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition. 2005;41(4):426–9. - PubMed
-
- Schwimmer JB, Deutsch R, Kahen T, Lavine JE, Stanley C, Behling C. Prevalence of fatty liver in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2006;118(4):1388–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

