Dexmedetomidine versus Midazolam in Procedural Sedation. A Systematic Review of Efficacy and Safety
- PMID: 28107373
- PMCID: PMC5249234
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169525
Dexmedetomidine versus Midazolam in Procedural Sedation. A Systematic Review of Efficacy and Safety
Abstract
Objectives: To systematically review the literature comparing the efficacy and safety of dexmedetomidine and midazolam when used for procedural sedation.
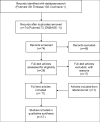
Materials and methods: We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE and COCHRANE for clinical trials comparing dexmedetomidine and midazolam for procedural sedation up to June 20, 2016. Inclusion criteria: clinical trial, human subjects, adult subjects (≥18 years), article written in English, German, French or Dutch, use of study medication for conscious sedation and at least one group receiving dexmedetomidine and one group receiving midazolam. Exclusion criteria: patients in intensive care, pediatric subjects and per protocol use of additional sedative medication other than rescue medication. Outcome measures for efficacy comparison were patient and clinician satisfaction scores and pain scores; outcome measures for safety comparison were hypotension, hypoxia, and circulatory and respiratory complications.
Results: We identified 89 papers, of which 12 satisfied the inclusion and exclusion criteria; 883 patients were included in these studies. Dexmedetomidine was associated with higher patient and operator satisfaction than midazolam. Patients receiving dexmedetomidine experienced less pain and had lower analgesic requirements. Respiratory and hemodynamic safety were similar.
Conclusions: Dexmedetomidine is a promising alternative to midazolam for use in procedural sedation. Dexmedetomidine provides more comfort during the procedure for the patient and clinician. If carefully titrated, the safety profiles are similar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
References
-
- Miller RD. Miller's Anesthesia. Philadelphia, Pa.; Edinburgh: Elsevier Saunders; 2009.
-
- Lodenius A, Ebberyd A, Hardemark Cedborg A, Hagel E, Mkrtchian S, Christensson E, et al. Sedation with Dexmedetomidine or Propofol Impairs Hypoxic Control of Breathing in Healthy Male Volunteers: A Nonblinded, Randomized Crossover Study. Anesthesiology. 2016;125: 700–715. 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001236 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996;17: 1–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases