Changes in Molecular Characteristics of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in Clinical Specimens from Children in Beijing between 2003 and 2015
- PMID: 28107399
- PMCID: PMC5249184
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170253
Changes in Molecular Characteristics of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in Clinical Specimens from Children in Beijing between 2003 and 2015
Abstract
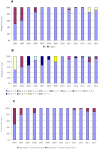
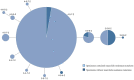
The molecular characteristics of 480 Mycoplasma pneumoniae polymerase chain reaction-positive specimens (331 were previously reported and 149 were newly reported) collected from pediatric patients in Beijing, China, between 2003 and 2015 were analyzed. Genotype M4-5-7-2/P1 were the most prevalent across the 13-year study period, although the isolation and mutation rates for this genotype varied between the periods 2003-2007, 2008-2013, and 2014-2015. In addition, there was a close association between the M4-5-7-2 genotype and macrolide resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Waites KB, Atkinson TP. The role of Mycoplasma in upper respiratory infections. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 200911:198–206. - PubMed
-
- Lenglet A, Herrador Z, Magiorakos AP, Leitmeyer K, Coulombier D. Surveillance status and recent data for Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in the European Union and European Economic Area, January 2012. Eurosurveillance 201217: pii:20075. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

