Biology of high single doses of IORT: RBE, 5 R's, and other biological aspects
- PMID: 28107823
- PMCID: PMC5251326
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-016-0750-3
Biology of high single doses of IORT: RBE, 5 R's, and other biological aspects
Abstract
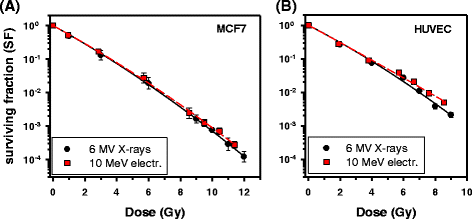
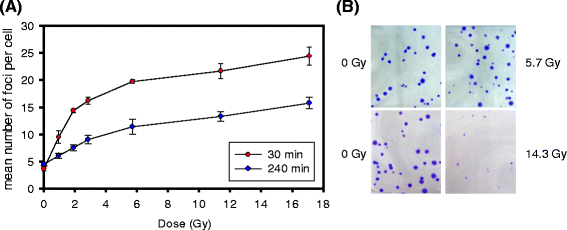
Intraoperative radiotherapy differs from conventional, fractionated radiotherapy in several aspects that may influence its biological effect. The radiation quality influences the relative biologic effectiveness (RBE), and the role of the five R's of radiotherapy (reassortment, repair, reoxygenation, repopulation, radiosensitivity) is different. Furthermore, putative special biological effects and the small volume receiving a high single dose may be important. The present review focuses on RBE, repair, and repopulation, and gives an overview of the other factors that potentially contribute to the efficacy. The increased RBE should be taken into account for low-energy X-rays while evidence of RBE < 1 for high-energy electrons at higher doses is presented. Various evidence supports a hypothesis that saturation of the primary DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair mechanisms leads to increasing use of an error-prone backup repair system leading to genomic instability that may contribute to inactivate tumour cells at high single doses. Furthermore, the elimination of repopulation of residual tumour cells in the tumour bed implies that some patients are likely to have very few residual tumour cells which may be cured even by low doses to the tumour bed. The highly localised dose distribution of IORT has the potential to inactivate tumour cells while sparing normal tissue by minimising the volume exposed to high doses. Whether special effects of high single doses also contribute to the efficacy will require further experimental and clinical studies.
Figures


References
-
- Withers HR. The four R’s of radiotherapy. In: Lett JT, Adler H, editors. Advances in Radiation Biology, Vol. 5. New York: Academic Press; 1975. p. 241–71.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

