Metabolic biomarker signature to differentiate pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma from chronic pancreatitis
- PMID: 28108468
- PMCID: PMC5754849
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312432
Metabolic biomarker signature to differentiate pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma from chronic pancreatitis
Erratum in
-
Correction: Metabolic biomarker signature to differentiate pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma from chronic pancreatitis.Gut. 2018 May;67(5):994. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312432corr1. Gut. 2018. PMID: 29626085 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: Current non-invasive diagnostic tests can distinguish between pancreatic cancer (pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC)) and chronic pancreatitis (CP) in only about two thirds of patients. We have searched for blood-derived metabolite biomarkers for this diagnostic purpose.
Design: For a case-control study in three tertiary referral centres, 914 subjects were prospectively recruited with PDAC (n=271), CP (n=282), liver cirrhosis (n=100) or healthy as well as non-pancreatic disease controls (n=261) in three consecutive studies. Metabolomic profiles of plasma and serum samples were generated from 477 metabolites identified by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
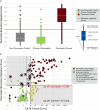
Results: A biomarker signature (nine metabolites and additionally CA19-9) was identified for the differential diagnosis between PDAC and CP. The biomarker signature distinguished PDAC from CP in the training set with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.96 (95% CI 0.93-0.98). The biomarker signature cut-off of 0.384 at 85% fixed specificity showed a sensitivity of 94.9% (95% CI 87.0%-97.0%). In the test set, an AUC of 0.94 (95% CI 0.91-0.97) and, using the same cut-off, a sensitivity of 89.9% (95% CI 81.0%-95.5%) and a specificity of 91.3% (95% CI 82.8%-96.4%) were achieved, successfully validating the biomarker signature.
Conclusions: In patients with CP with an increased risk for pancreatic cancer (cumulative incidence 1.95%), the performance of this biomarker signature results in a negative predictive value of 99.9% (95% CI 99.7%-99.9%) (training set) and 99.8% (95% CI 99.6%-99.9%) (test set). In one third of our patients, the clinical use of this biomarker signature would have improved diagnosis and treatment stratification in comparison to CA19-9.
Keywords: PANCREATIC CANCER; PANCREATITIS.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures



Comment in
-
A metabolomics-based biomarker signature discriminates pancreatic cancer from chronic pancreatitis.Gut. 2018 Jan;67(1):2-3. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313665. Epub 2017 May 24. Gut. 2018. PMID: 28539352 No abstract available.
References
-
- Duffy MJ, Sturgeon C, Lamerz R, et al. Tumor markers in pancreatic cancer: a European Group on Tumor Markers (EGTM) status report. Ann Oncol 2010;21:441–7. - PubMed
-
- Gui JC, Yan WL, Liu XD. CA19-9 and CA242 as tumor markers for the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis. Clin Exp Med 2013;14:225–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
