Fungal periprosthetic joint infection following total elbow arthroplasty: a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 28109195
- PMCID: PMC5251295
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-016-1176-0
Fungal periprosthetic joint infection following total elbow arthroplasty: a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: With improving surgical techniques for total elbow arthroplasty clinical outcomes have improved and its utilization continues to increase. Despite these advances, complication rates remain as high as 24%. Of these complications periprosthetic joint infection is one of the most common and morbid. The rheumatoid elbow remains a leading indication for total elbow arthroplasty. Patients with this condition frequently require immunosuppressive therapy, which places them at higher risk of both typical and atypical infections.
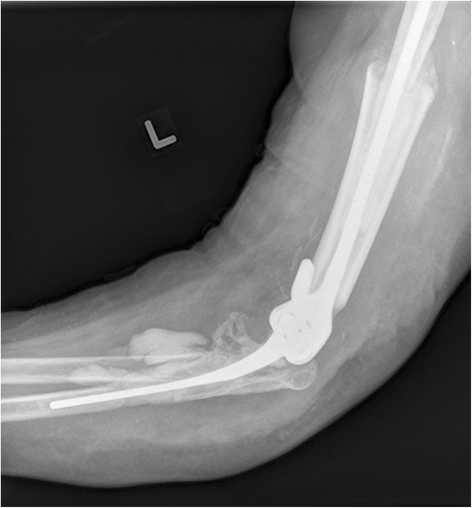
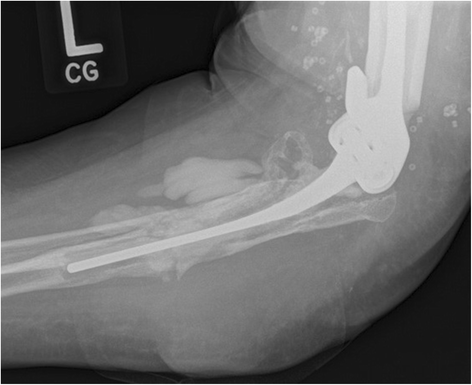
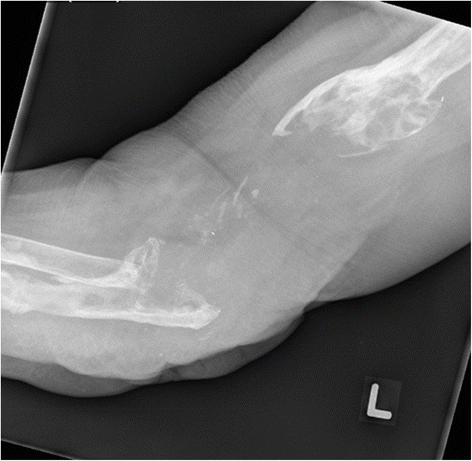
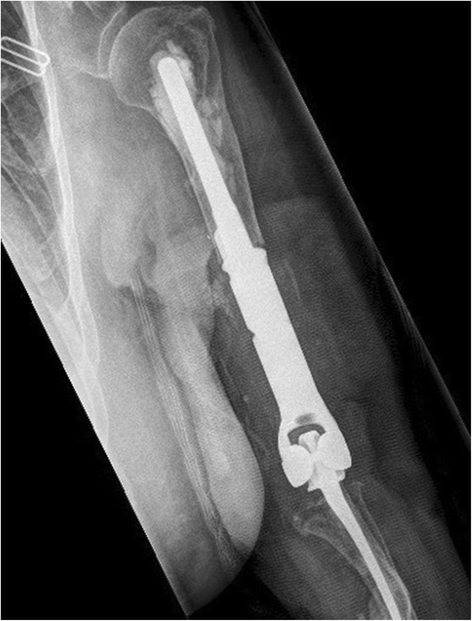
Case presentation: We present the case of a persistent, late-onset periprosthetic joint infection in a total elbow arthroplasty of a 64-year-old Caucasian woman with severe refractory rheumatoid arthritis. The offending pathogen, Aspergillus terreus, is previously unreported in the arthroplasty literature and grew concurrently with coagulase-negative staphylococcus. Eradication of the fungal and bacterial agents involved resection arthroplasty, serial debridement, and multiple courses of intravenous and oral antimicrobial therapy. Two attempts at reimplantation arthroplasty failed to eliminate the infection and our patient ultimately required definitive resection arthroplasty.
Conclusions: Arthroplasty in the rheumatoid elbow confers with it a high complication rate. Inflammatory disease and immunosuppressive drugs combined with the subcutaneous anatomy of the elbow contribute to the risk of infection. Fungal periprosthetic joint infection in the rheumatoid patient presents both diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. Fungal growth should always be treated and requires organism-specific antimicrobials in conjunction with surgical debridement. More literature is needed to determine the optimal treatment regimen for this devastating complication.
Keywords: Aspergillus terreus; Fungal; Infection; Periprosthetic joint infection; Resection arthroplasty; Revision; Rheumatoid arthritis; Total elbow arthroplasty.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

