Estimated Prevalence of Insomnia among Women Veterans: Results of a Postal Survey
- PMID: 28110799
- PMCID: PMC5435535
- DOI: 10.1016/j.whi.2016.12.003
Estimated Prevalence of Insomnia among Women Veterans: Results of a Postal Survey
Abstract
Objectives: Insomnia is a significant public health concern known to particularly impact women and the veteran population; however, rates of insomnia disorder among women veterans are not known.
Method: Women veterans who had received health care at VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System between 2008 and 2010 and resided within 25 miles of the facility were sent a postal survey assessing sleep, demographics, and other related patient characteristics.
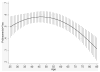
Results: A total of 660 women (43.1% of potential responders) returned the postal survey and provided sufficient information for insomnia diagnosis. On average, women reported 6.2 hours of sleep per night. The prevalence of insomnia, determined according to diagnostic criteria from the International Classification of Sleep Disorders-2, was 52.3%. Women with insomnia reported more severely disturbed sleep, and more pain, menopausal symptoms, stress/worries, and nightmares compared with women without insomnia. There was a quadratic relationship between age and insomnia with women in their mid-40s, most likely to have insomnia.
Conclusions: This survey study found that insomnia symptoms were endorsed by more than one-half of the women veterans in this sample of VA users, highlighting the critical need for enhanced clinical identification and intervention. Further research is needed to establish national rates of insomnia among women veterans and to improve access to evidence-based treatment of insomnia disorder.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

References
-
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine. The international classification of sleep disorders. 2. Westchester, IL: American Academy of Sleep Medicine; 2005. I. Insomnia; pp. 1–31.
-
- Bean-Mayberry B, Yano EM, Washington DL, Goldzweig C, Batuman F, Huang C, … Shekelle PG. Systematic review of women veterans’ health: Update on successes and gaps. Women’s Health Issues. 2011;21:S84–S97. - PubMed
-
- Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF, Monk TH, Berman SR, Kupfer DJ. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Research. 1989;28(2):193–213. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

