Recapitulation of Clinical Individual Susceptibility to Drug-Induced QT Prolongation in Healthy Subjects Using iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes
- PMID: 28111276
- PMCID: PMC5312248
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.12.014
Recapitulation of Clinical Individual Susceptibility to Drug-Induced QT Prolongation in Healthy Subjects Using iPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes
Abstract
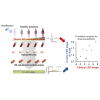
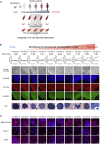
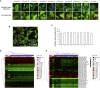
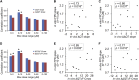
To predict drug-induced serious adverse events (SAE) in clinical trials, a model using a panel of cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) of individuals with different susceptibilities could facilitate major advancements in translational research in terms of safety and pharmaco-economics. However, it is unclear whether hiPSC-derived cells can recapitulate interindividual differences in drug-induced SAE susceptibility in populations not having genetic disorders such as healthy subjects. Here, we evaluated individual differences in SAE susceptibility based on an in vitro model using hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) as a pilot study. hiPSCs were generated from blood samples of ten healthy volunteers with different susceptibilities to moxifloxacin (Mox)-induced QT prolongation. Different Mox-induced field potential duration (FPD) prolongation values were observed in the hiPSC-CMs from each individual. Interestingly, the QT interval was significantly positively correlated with FPD at clinically relevant concentrations (r > 0.66) in multiple analyses including concentration-QT analysis. Genomic analysis showed no interindividual significant differences in known target-binding sites for Mox and other drugs such as the hERG channel subunit, and baseline QT ranges were normal. The results suggest that hiPSC-CMs from healthy subjects recapitulate susceptibility to Mox-induced QT prolongation and provide proof of concept for in vitro preclinical trials.
Keywords: QT prolongation; cardiomyocytes; clinical trial; drug safety assessment; drug susceptibility; iPSC; inter-individual difference.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Braam S.R., Tertoolen L., van de Stolpe A., Meyer T., Passier R., Mummery C.L. Prediction of drug-induced cardiotoxicity using human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Stem Cell Res. 2010;4:107–116. - PubMed
-
- Burke J.H., Ehlert F.A., Kruse J.T., Parker M.A., Goldberger J.J., Kadish A.H. Gender-specific differences in the QT interval and the effect of autonomic tone and menstrual cycle in healthy adults. Am. J. Cardiol. 1997;79:178–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

