Measles and rubella elimination in the WHO Region for Europe: progress and challenges
- PMID: 28111293
- PMCID: PMC6434680
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmi.2017.01.003
Measles and rubella elimination in the WHO Region for Europe: progress and challenges
Abstract
Globally measles remains one of the leading causes of death among young children even though a safe and cost-effective vaccine is available. The World Health Organization (WHO) European Region has seen a decline in measles and rubella cases in recent years. The recent outbreaks have primarily affected adolescents and young adults with no vaccination or an incomplete vaccination history. Eliminating measles and rubella is one of the top immunization priorities of the European Region as outlined in the European Vaccine Action Plan 2015-2020. Following the 2010 decision by the Member States in the Region to initiate the process of verifying elimination, the European Regional Verification Commission for Measles and Rubella Elimination (RVC) was established in 2011. The RVC meets every year to evaluate the status of measles and rubella elimination in the Region based on documentation submitted by each country's National Verification Committees. The verification process was however modified in late 2014 to assess the elimination status at the individual country level instead of at regional level. The WHO European Region has made substantial progress towards measles and rubella elimination over the past 5 years. The RVC's conclusion in 2016 that 70% and 66% of the 53 Member States in the Region had interrupted the endemic transmission of measles and rubella, respectively, by 2015 is a testament to this progress. Nevertheless, where measles and rubella remain endemic, challenges in vaccination service delivery and disease surveillance will need to be addressed through focused technical assistance from WHO and development partners.
Keywords: Disease elimination; European Region; Measles; Progress; Rubella; Vaccination; Verification.
Copyright © 2017 European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Transparency declaration
The authors declare no conflicts of interest and also that no external funding was received in preparation of this manuscript.
Figures


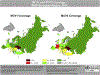

References
-
- World Health Organization. Progress in global control and regional elimination of measles, 2000–2011. Wkly Epidemiol Rec 2013;88:29–36. Available at: http://www.who.int/wer/2013/wer8803.pdf. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Measles fact sheet, reviewed March 2016 Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs286/en/.
-
- World Health Organization. Global vaccine action plan. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2012. Available at: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/78141/1/9789241504980_eng.pdf?ua=1.
-
- World Health Organization. Global measles and rubella strategic plan: 2012–2020. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2012. Available at: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/44855/1/9789241503396_eng.pdf.
-
- PAHO & WHO Americas, Region of Americas is declared free of measles. Available at: http://www.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=1252....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

