Does Bt rice pose risks to non-target arthropods? Results of a meta-analysis in China
- PMID: 28111920
- PMCID: PMC5506656
- DOI: 10.1111/pbi.12698
Does Bt rice pose risks to non-target arthropods? Results of a meta-analysis in China
Abstract
Transgenic Bt rice expressing the insecticidal proteins derived from Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner (Bt) has been developed since 1989. Their ecological risks towards non-target organisms have been investigated; however, these studies were conducted individually, yielding uncertainty regarding potential agroecological risks associated with large-scale deployment of Bt rice lines. Here, we developed a meta-analysis of the existing literature to synthesize current knowledge of the impacts of Bt rice on functional arthropod guilds, including herbivores, predators, parasitoids and detritivores in laboratory and field studies. Laboratory results indicate Bt rice did not influence survival rate and developmental duration of herbivores, although exposure to Bt rice led to reduced egg laying, which correctly predicted their reduced abundance in Bt rice agroecosystems. Similarly, consuming prey exposed to Bt protein did not influence survival, development or fecundity of predators, indicating constant abundances of predators in Bt rice fields. Compared to control agroecosystems, parasitoid populations decreased slightly in Bt rice cropping systems, while detritivores increased. We draw two inferences. One, laboratory studies of Bt rice showing effects on ecological functional groups are mainly either consistent with or more conservative than results of field studies, and two, Bt rice will pose negligible risks to the non-target functional guilds in future large-scale Bt rice agroecosystems in China.
Keywords: Bt rice; functional guilds; meta-analysis; non-target.
© 2017 The Authors. Plant Biotechnology Journal published by Society for Experimental Biology and The Association of Applied Biologists and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

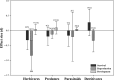
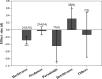

References
-
- Abràmoff, M.D. , Magalhães, P.J. and Ram, S.J. (2004) Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int. 11, 36–42.
-
- Bai, Y.Y. , Yan, R.H. , Ye, G.Y. , Huang, F.N. , Wangila, D.S. , Wang, J.J. and Cheng, J.A. (2012) Field response of aboveground non‐target arthropod community to transgenic Bt‐Cry1Ab rice plant residues in postharvest seasons. Transgenic Res. 21, 1023–1032. - PubMed
-
- Begg, C.B. and Mazumdar, M. (1994) Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics, 50, 1088–1101. - PubMed
-
- Borenstein, M. , Hedges, L.V. , Higgins, J. and Rothstein, H.R. (2009) Introduction to Meta‐analysis. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. https://www.meta-analysis-workshops.com/download/bookChapterSample.pdf [Accessed 2 September 2016]
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

