Progression-related loss of stromal Caveolin 1 levels fosters the growth of human PC3 xenografts and mediates radiation resistance
- PMID: 28112237
- PMCID: PMC5255553
- DOI: 10.1038/srep41138
Progression-related loss of stromal Caveolin 1 levels fosters the growth of human PC3 xenografts and mediates radiation resistance
Abstract
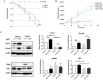
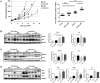
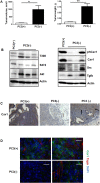
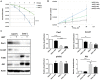
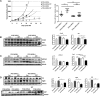
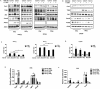
Despite good treatment results in localized prostate tumors, advanced disease stages usually have a pronounced resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. The membrane protein caveolin-1 (Cav1) functions here as an important oncogene. Therefore we examined the impact of stromal Cav1 expression for tumor growth and sensitivity to ionizing radiation (IR). Silencing of Cav1 expression in PC3 cells resulted in increased tumor growth and a reduced growth delay after IR when compared to tumors generated by Cav1-expressing PC3 cells. The increased radiation resistance was associated with increasing amounts of reactive tumor stroma and a Cav1 re-expression in the malignant epithelial cells. Mimicking the human situation these results were confirmed using co-implantation of Cav1-silenced PC3 cells with Cav1-silenced or Cav1-expressing fibroblasts. Immunohistochemically analysis of irradiated tumors as well as human prostate tissue specimen confirmed that alterations in stromal-epithelial Cav1 expressions were accompanied by a more reactive Cav1-reduced tumor stroma after radiation and within advanced prostate cancer tissues which potentially mediates the resistance to radiation treatment. Conclusively, the radiation response of human prostate tumors is critically regulated by Cav1 expression in stromal fibroblasts. Loss of stromal Cav1 expression in advanced tumor stages may thus contribute to resistance of these tumors to radiotherapy.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

