Combined small-molecule inhibition accelerates the derivation of functional cortical neurons from human pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 28112759
- PMCID: PMC5516899
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.3777
Combined small-molecule inhibition accelerates the derivation of functional cortical neurons from human pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
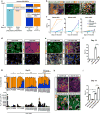
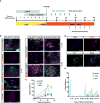
Considerable progress has been made in converting human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) into functional neurons. However, the protracted timing of human neuron specification and functional maturation remains a key challenge that hampers the routine application of hPSC-derived lineages in disease modeling and regenerative medicine. Using a combinatorial small-molecule screen, we previously identified conditions to rapidly differentiate hPSCs into peripheral sensory neurons. Here we generalize the approach to central nervous system (CNS) fates by developing a small-molecule approach for accelerated induction of early-born cortical neurons. Combinatorial application of six pathway inhibitors induces post-mitotic cortical neurons with functional electrophysiological properties by day 16 of differentiation, in the absence of glial cell co-culture. The resulting neurons, transplanted at 8 d of differentiation into the postnatal mouse cortex, are functional and establish long-distance projections, as shown using iDISCO whole-brain imaging. Accelerated differentiation into cortical neuron fates should facilitate hPSC-based strategies for disease modeling and cell therapy in CNS disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center has filed provisional patent application (US PRO 62/287821) on the methods described in the manuscript.
Figures



References
-
- Menendez L, Yatskievych TA, Antin PB, Dalton S. Wnt signaling and a Smad pathway blockade direct the differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells to multipotent neural crest cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2011;108:19240–19245. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sun L, et al. Design, synthesis, and evaluations of substituted 3-[(3- or 4-carboxyethylpyrrol-2-yl)methylidenyl]indolin-2-ones as inhibitors of VEGF, FGF, and PDGF receptor tyrosine kinases. Journal of medicinal chemistry. 1999;42:5120–5130. - PubMed
METHODS ONLY REFERENCES
-
- Kaech S, Banker G. Culturing hippocampal neurons. Nat Protoc. 2006;1:2406–2415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

