Oxidation of [U-13 C]glucose in the human brain at 7T under steady state conditions
- PMID: 28112825
- PMCID: PMC5522773
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.26603
Oxidation of [U-13 C]glucose in the human brain at 7T under steady state conditions
Abstract
Purpose: Disorders of brain energy metabolism and neurotransmitter recycling have been implicated in multiple neurological conditions. 13 C magnetic resonance spectroscopy (13 C MRS) during intravenous administration of 13 C-labeled compounds has been used to measure turnover rates of brain metabolites. This approach, however, requires prolonged infusion inside the magnet. Proton decoupling is typically required but may be difficult to implement with standard equipment. We examined an alternative approach to monitor glucose metabolism in the human brain.
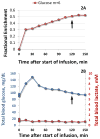
Methods: 13 C-enriched glucose was infused in healthy subjects outside the magnet to a steady-state level of 13 C enrichment. Subsequently, the subjects were scanned at 7T for 60 min without 1 H decoupling. Metabolic modeling was used to calculate anaplerosis.
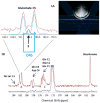
Results: Biomarkers of energy metabolism and anaplerosis were detected. The glutamate C5 doublet provided information about glucose-derived acetyl-coenzyme A flux into the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle via pyruvate dehydrogenase, and the bicarbonate signal reflected overall TCA cycle activity. The glutamate C1/C5 ratio is sensitive to anaplerosis.
Conclusion: Brain 13 C MRS at 7T provides information about glucose oxidation and anaplerosis without the need of prolonged 13 C infusions inside the scanner and without technical challenges of 1 H decoupling, making it a feasible approach for clinical research. Magn Reson Med 78:2065-2071, 2017. © 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Keywords: 13C MRS; 13C bicarbonate; 7 Tesla; TCA cycle; brain energy metabolism.
© 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures


References
-
- Phelps ME, Huang SC, Hoffman EJ, Selin C, Sokoloff L, Kuhl DE. Tomographic Measurement of Local Cerebral Glucose Metabolic-Rate in Humans with (F-18)2-Fluoro-2-Deoxy-D-Glucose - Validation of Method. Ann Neurol. 1979;6(5):371–388. - PubMed
-
- Glenn TC, Kelly DF, Boscardin WJ, McArthur DL, Vespa P, Oertel M, Hovda DA, Bergsneider M, Hillered L, Martin NA. Energy dysfunction as a predictor of outcome after moderate or severe head injury: indices of oxygen, glucose, and lactate metabolism. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 2003;23(10):1239–1250. - PubMed
-
- Gallagher CN, Carpenter KL, Grice P, Howe DJ, Mason A, Timofeev I, Menon DK, Kirkpatrick PJ, Pickard JD, Sutherland GR, Hutchinson PJ. The human brain utilizes lactate via the tricarboxylic acid cycle: a 13C-labelled microdialysis and high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance study. Brain. 2009;132(Pt 10):2839–2849. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

