Autophagy in renal tubular injury and repair
- PMID: 28112877
- PMCID: PMC7814874
- DOI: 10.1111/apha.12852
Autophagy in renal tubular injury and repair
Abstract
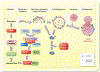
Autophagy is a fundamental cellular process that maintains normal function and structure of the cell. It can be induced during stress and serves as an adaptive response for cell survival. Normal kidneys have high metabolic demands yet are relatively hypoxic, especially in the medulla and papilla. Injury or ageing aggravates metabolic perturbation and activates autophagy in many types of renal cells. In the kidney, tubular epithelial cells consume the most energy due to active transport mechanisms and therefore are the most susceptible to injuries from hypoxic or low-energy states. This brief review will summarize current understandings of the biological function and molecular regulation of epithelial autophagy during tubular injury and repair.
Keywords: autophagy; kidney; stress response; tubular injury.
© 2017 Scandinavian Physiological Society. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The author declares no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bolignano D, Mattace-Raso F, Sijbrands EJ & Zoccali C 2014. The aging kidney revisited: a systematic review. Ageing Res Rev 14, 65–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

