Efficient Descriptor-Based Segmentation of Parotid Glands With Nonlocal Means
- PMID: 28113224
- PMCID: PMC5469701
- DOI: 10.1109/TBME.2016.2603119
Efficient Descriptor-Based Segmentation of Parotid Glands With Nonlocal Means
Abstract
Objective: We introduce descriptor-based segmentation that extends existing patch-based methods by combining intensities, features, and location information. Since it is unclear which image features are best suited for patch selection, we perform a broad empirical study on a multitude of different features.
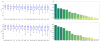
Methods: We extend nonlocal means segmentation by including image features and location information. We search larger windows with an efficient nearest neighbor search based on kd-trees. We compare a large number of image features.
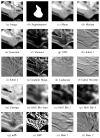
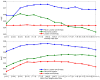
Results: The best results were obtained for entropy image features, which have not yet been used for patch-based segmentation. We further show that searching larger image regions with an approximate nearest neighbor search and location information yields a significant improvement over the bounded nearest neighbor search traditionally employed in patch-based segmentation methods.
Conclusion: Features and location information significantly increase the segmentation accuracy. The best features highlight boundaries in the image.
Significance: Our detailed analysis of several aspects of nonlocal means-based segmentation yields new insights about patch and neighborhood sizes together with the inclusion of location information. The presented approach advances the state-of-the-art in the segmentation of parotid glands for radiation therapy planning.
Figures





References
-
- Heckemann R, et al. Automatic anatomical brain MRI segmentation combining label propagation and decision fusion. Neuro Image. 2006;33(1):115–126. - PubMed
-
- Rohlfing T, et al. Quo vadis, atlas-based segmentation? Handbook of Biomedical Image Analysis. 2005:435–486.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

