Gsk3 is a metabolic checkpoint regulator in B cells
- PMID: 28114292
- PMCID: PMC5310963
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.3664
Gsk3 is a metabolic checkpoint regulator in B cells
Abstract
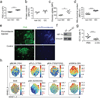
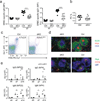
B cells predominate in a quiescent state until an antigen is encountered, which results in rapid growth, proliferation and differentiation of the B cells. These distinct cell states are probably accompanied by differing metabolic needs, yet little is known about the metabolic control of B cell fate. Here we show that glycogen synthase kinase 3 (Gsk3) is a metabolic sensor that promotes the survival of naive recirculating B cells by restricting cell mass accumulation. In antigen-driven responses, Gsk3 was selectively required for regulation of B cell size, mitochondrial biogenesis, glycolysis and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), in a manner mediated by the co-stimulatory receptor CD40. Gsk3 was required to prevent metabolic collapse and ROS-induced apoptosis after glucose became limiting, functioning in part by repressing growth dependent on the myelocytomatosis oncoprotein c-Myc. Notably, we found that Gsk3 was required for the generation and maintenance of germinal center B cells, which require high glycolytic activity to support growth and proliferation in a hypoxic microenvironment.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

