A Unique Egg Cortical Granule Localization Motif Is Required for Ovastacin Sequestration to Prevent Premature ZP2 Cleavage and Ensure Female Fertility in Mice
- PMID: 28114310
- PMCID: PMC5293279
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006580
A Unique Egg Cortical Granule Localization Motif Is Required for Ovastacin Sequestration to Prevent Premature ZP2 Cleavage and Ensure Female Fertility in Mice
Abstract
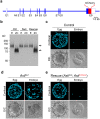
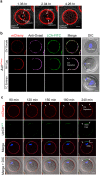
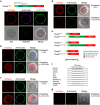
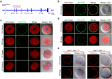
Monospermic fertilization is mediated by the extracellular zona pellucida composed of ZP1, ZP2 and ZP3. Sperm bind to the N-terminus of ZP2 which is cleaved after fertilization by ovastacin (encoded by Astl) exocytosed from egg cortical granules to prevent sperm binding. AstlNull mice lack the post-fertilization block to sperm binding and the ability to rescue this phenotype with AstlmCherry transgenic mice confirms the role of ovastacin in providing a definitive block to polyspermy. During oogenesis, endogenous ovastacin traffics through the endomembrane system prior to storage in peripherally located cortical granules. Deletion mutants of ovastacinmCherry expressed in growing oocytes define a unique 7 amino acid motif near its N-terminus that is necessary and sufficient for cortical granule localization. Deletion of the 7 amino acids by CRISPR/Cas9 at the endogenous locus (AstlΔ) prevents cortical granule localization of ovastacin. The misdirected enzyme is present within the endomembrane system and ZP2 is prematurely cleaved. Sperm bind poorly to the zona pellucida of AstlΔ/Δ mice with partially cleaved ZP2 and female mice are sub-fertile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exist.
Figures
References
-
- Stewart-Savage J, Bavister BD. A cell surface block to polyspermy occurs in golden hamster eggs. Dev Biol. 1988;128:150–7. - PubMed
-
- Maleszewski M, Kimura Y, Yanagimachi R. Sperm membrane incorporation into oolemma contributes to the oolemma block to sperm penetration: evidence based on intracytoplasmic sperm injection experiments in the mouse. Mol Reprod Dev. 1996;44(2):256–9. 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2795(199606)44:2<256::AID-MRD16>3.0.CO;2-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ducibella T, Huneau D, Angelichio E, Xu Z, Schultz RM, Kopf GS, et al. Egg-to-embryo transition is driven by differential responses to Ca(2+) oscillation number. Dev Biol. 2002;250(2):280–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

