Polyporus squamosus Lectin 1a (PSL1a) Exhibits Cytotoxicity in Mammalian Cells by Disruption of Focal Adhesions, Inhibition of Protein Synthesis and Induction of Apoptosis
- PMID: 28114329
- PMCID: PMC5256987
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170716
Polyporus squamosus Lectin 1a (PSL1a) Exhibits Cytotoxicity in Mammalian Cells by Disruption of Focal Adhesions, Inhibition of Protein Synthesis and Induction of Apoptosis
Abstract
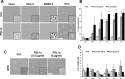
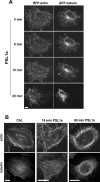
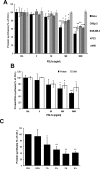
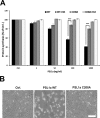
PSL1a is a lectin from the mushroom Polyporus squamosus that binds to sialylated glycans and glycoconjugates with high specificity and selectivity. In addition to its N-terminal carbohydrate-binding domain, PSL1a possesses a Ca2+-dependent proteolytic activity in the C-terminal domain. In the present study, we demonstrate that PSL1a has cytotoxic effects on mammalian cancer cells, and we show that the cytotoxicity is dependent on the cysteine protease activity. PSL1a treatment leads to cell rounding and detachment from the substratum, concomitant with disruption of vinculin complexes in focal adhesions. We also demonstrate that PSL1a inhibits protein synthesis and induces apoptosis in HeLa cells, in a time- and concentration-dependent manner.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Goldstein IJ, Hughes R. C., Monsigny M., Osawa T., and Sharon N. What should be called a lectin? Nature. 1980;66:285.
-
- Sharon N, Lis H. Lectins as cell recognition molecules. Science. 1989;246(4927):227–34. - PubMed
-
- Dam TK, Roy R, Das SK, Oscarson S, Brewer CF. Binding of multivalent carbohydrates to concanavalin A and Dioclea grandiflora lectin. Thermodynamic analysis of the "multivalency effect". J Biol Chem. 2000;275(19):14223–30. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

