Compound 49b Regulates ZO-1 and Occludin Levels in Human Retinal Endothelial Cells and in Mouse Retinal Vasculature
- PMID: 28114578
- PMCID: PMC5256679
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.16-20412
Compound 49b Regulates ZO-1 and Occludin Levels in Human Retinal Endothelial Cells and in Mouse Retinal Vasculature
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate whether Epac1 is key to Compound 49b's regulation of zonula occluden 1 (ZO-1) and occludin levels in human retinal endothelial cells (REC) and in an Epac1 vascular-specific conditional knockout mouse retina.
Methods: Primary REC were grown in normal (5 mM) or high glucose (25 mM). Some cells were treated with a novel β-adrenergic receptor agonist, Compound 49b. Additional dishes were treated with Epac1 siRNA or Compound 49b + Epac1 siRNA. Protein levels of ZO-1, occludin, VEGF, and protein kinase C zeta (PKCz) were measured by Western blotting. Cell permeability was measured in REC grown in normal or high glucose and treated with Compound 49b, a specific Epac 1 agonist (8-CPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP), or VEGF. Epac1 floxed and cdh5-Cre mice were bred to generate Epac1 knockout mice in vascular endothelial cells. Immunofluorescence was done on retinal flatmounts from the floxed and Cre-Lox mice for occludin and ZO-1. Western blotting was also done for both proteins in whole retinal lysates from the mice.
Results: High glucose significantly reduced ZO-1 and occludin protein levels, which was associated with reduced cell adhesion. Compound 49b increased endothelial cell barrier protein levels through active Epac1. Knockout of Epac1 in vascular endothelial cells substantially reduced ZO-1 and occludin staining in retinal flatmounts, as well as protein levels.
Conclusions: Compound 49b increased ZO-1 and occludin protein levels, likely leading to decreased permeability.
Figures

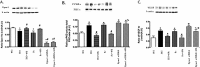


Similar articles
-
Toll-Like Receptor 4 Reduces Occludin and Zonula Occludens 1 to Increase Retinal Permeability Both in vitro and in vivo.J Vasc Res. 2017;54(6):367-375. doi: 10.1159/000480455. Epub 2017 Nov 15. J Vasc Res. 2017. PMID: 29136627 Free PMC article.
-
miR-15a/16 inhibits TGF-beta3/VEGF signaling and increases retinal endothelial cell barrier proteins.Vision Res. 2017 Oct;139:23-29. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2017.07.007. Epub 2017 Aug 7. Vision Res. 2017. PMID: 28774775 Free PMC article.
-
Epac1 regulates TLR4 signaling in the diabetic retinal vasculature.Cytokine. 2021 Aug;144:155576. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155576. Epub 2021 May 18. Cytokine. 2021. PMID: 34020266 Free PMC article.
-
Association of reduced Connexin 43 expression with retinal vascular lesions in human diabetic retinopathy.Exp Eye Res. 2016 May;146:103-106. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2015.12.011. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Exp Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 26738943 Review.
-
The Role of Endothelial Senescence in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Retinopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 29;26(11):5211. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115211. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508021 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Scutellarein alleviates the dysfunction of inner blood-retinal-barrier initiated by hyperglycemia-stimulated microglia cells.Int J Ophthalmol. 2020 Oct 18;13(10):1538-1545. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2020.10.05. eCollection 2020. Int J Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 33078102 Free PMC article.
-
Qingchang Wenzhong Decoction Attenuates DSS-Induced Colitis in Rats by Reducing Inflammation and Improving Intestinal Barrier Function via Upregulating the MSP/RON Signalling Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:4846876. doi: 10.1155/2017/4846876. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 29234405 Free PMC article.
-
Semaphorin 7a regulates inflammatory mediators and permeability in retinal endothelial cells.Microvasc Res. 2023 Nov;150:104587. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2023.104587. Epub 2023 Jul 13. Microvasc Res. 2023. PMID: 37453650 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium butyrate inhibits activation of ROS/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway and angiogenesis in human retinal microvascular endothelial cells.Int Ophthalmol. 2025 Mar 18;45(1):108. doi: 10.1007/s10792-025-03458-w. Int Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40100328
-
Disruption of tight junctions contributes to hyposalivation of salivary glands in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes.J Anat. 2020 Sep;237(3):556-567. doi: 10.1111/joa.13203. Epub 2020 May 6. J Anat. 2020. PMID: 32374057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Diabetes Association. Eye Complications (2013). Available at: http://www.diabetes.org/living-with-diabetes/complications/eye-complicat....
-
- Erickson KK,, Sundstrom JM,, Antonetti DA. Vascular permeability in ocular disease and the role of tight junctions. Angiogenesis. 2007; 10: 103–117. - PubMed
-
- Harhaj NS,, Felinski EA,, Wolpert EB,, et al. VEGF activation of protein kinase C stimulates occludin phosphorylation and contributes to endothelial permeability. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006; 47: 5106–5115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

