p97 Negatively Regulates NRF2 by Extracting Ubiquitylated NRF2 from the KEAP1-CUL3 E3 Complex
- PMID: 28115426
- PMCID: PMC5376629
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00660-16
p97 Negatively Regulates NRF2 by Extracting Ubiquitylated NRF2 from the KEAP1-CUL3 E3 Complex
Abstract
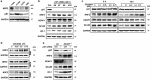
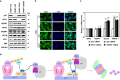
Activation of the stress-responsive transcription factor NRF2 is the major line of defense to combat oxidative or electrophilic insults. Under basal conditions, NRF2 is continuously ubiquitylated by the KEAP1-CUL3-RBX1 E3 ubiquitin ligase complex and is targeted to the proteasome for degradation (the canonical mechanism). However, the path from the CUL3 complex to ultimate proteasomal degradation was previously unknown. p97 is a ubiquitin-targeted ATP-dependent segregase that extracts ubiquitylated client proteins from membranes, protein complexes, or chromatin and has an essential role in autophagy and the ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS). In this study, we show that p97 negatively regulates NRF2 through the canonical pathway by extracting ubiquitylated NRF2 from the KEAP1-CUL3 E3 complex, with the aid of the heterodimeric cofactor UFD1/NPL4 and the UBA-UBX-containing protein UBXN7, for efficient proteasomal degradation. Given the role of NRF2 in chemoresistance and the surging interest in p97 inhibitors to treat cancers, our results indicate that dual p97/NRF2 inhibitors may offer a more potent and long-term avenue of p97-targeted treatment.
Keywords: KEAP1; NRF2; autophagy; cancer chemoresistance; oxidative stress; p97; proteasome; protein quality control; ubiquitylation.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



References
-
- Tebay LE, Robertson H, Durant ST, Vitale SR, Penning TM, Dinkova-Kostova AT, Hayes JD. 2015. Mechanisms of activation of the transcription factor Nrf2 by redox stressors, nutrient cues, and energy status and the pathways through which it attenuates degenerative disease. Free Radic Biol Med 88:108–146. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi A, Kang MI, Okawa H, Ohtsuji M, Zenke Y, Chiba T, Igarashi K, Yamamoto M. 2004. Oxidative stress sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Mol Cell Biol 24:7130–7139. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.16.7130-7139.2004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
