Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis: perspectives on patient selection in low- to middle-income countries
- PMID: 28115864
- PMCID: PMC5221809
- DOI: 10.2147/IJNRD.S104208
Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis: perspectives on patient selection in low- to middle-income countries
Abstract
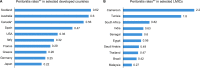
Chronic kidney disease is a major public health problem that continues to show an unrelenting global increase in prevalence. The prevalence of chronic kidney disease has been predicted to grow the fastest in low- to middle-income countries (LMICs). There is evidence that people living in LMICs have the highest need for renal replacement therapy (RRT) despite the lowest access to various modalities of treatment. As continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) does not require advanced technologies, much infrastructure, or need for dialysis staff support, it should be an ideal form of RRT in LMICs, particularly for those living in remote areas. However, CAPD is scarcely available in many LMICs, and even where available, there are several hurdles to be confronted regarding patient selection for this modality. High cost of CAPD due to unavailability of fluids, low patient education and motivation, low remuneration for nephrologists, lack of expertise/experience for catheter insertion and management of complications, presence of associated comorbid diseases, and various socio-demographic factors contribute significantly toward reduced patient selection for CAPD. Cost of CAPD fluids seems to be a major constraint given that many countries do not have the capacity to manufacture fluids but instead rely heavily on fluids imported from developed countries. There is need to invest in fluid manufacturing (either nationally or regionally) in LMICs to improve uptake of patients treated with CAPD. Workforce training and retraining will be necessary to ensure that there is coordination of CAPD programs and increase the use of protocols designed to improve CAPD outcomes such as insertion of catheters, treatment of peritonitis, and treatment of complications associated with CAPD. Training of nephrology workforce in CAPD will increase workforce experience and make CAPD a more acceptable RRT modality with improved outcomes.
Keywords: dialysis cost; dialysis fluid; nephrology workforce; peritoneal dialysis; peritonitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Jha V, Garcia-Garcia G, Iseki K, et al. Chronic kidney disease: global dimension and perspectives. Lancet. 2013;382(9888):260–272. - PubMed
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365(9455):217–223. - PubMed
-
- Liyanage T, Ninomiya T, Jha V, et al. Worldwide access to treatment for end-stage kidney disease: a systematic review. Lancet. 2015;385(9981):1975–1982. - PubMed
-
- Bargman JM, Thorpe KE, Churchill DN, Group CPDS. Relative contribution of residual renal function and peritoneal clearance to adequacy of dialysis: a reanalysis of the CANUSA study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12(10):2158–2162. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials