The Thyroid Na+/I- Symporter: Molecular Characterization and Genomic Regulation
- PMID: 28117294
- PMCID: PMC5283716
- DOI: 10.4274/2017.26.suppl.11
The Thyroid Na+/I- Symporter: Molecular Characterization and Genomic Regulation
Abstract
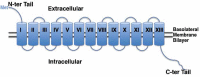
Iodide (I-) is an essential constituent of the thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), and the iodide concentrating mechanism of the thyroid gland is essential for the synthesis of these hormones. In addition, differential uptake of iodine isotopes (radioiodine) is a key modality for the diagnosis and therapy of thyroid cancer. The sodium dependent iodide transport activity of the thyroid gland is mainly attributed to the functional expression of the Na+/I- Symporter (NIS) localized at the basolateral membrane of thyrocytes. In this paper, we review and summarize current data on molecular characterization, on structure and function of NIS protein, as well as on the transcriptional regulation of NIS encoding gene in the thyroid gland. We also propose that a better and more precise understanding of NIS gene regulation at the molecular level in both healthy and malignant thyroid cells may lead to the identification of small molecule candidates. These could then be translated into clinical practice for better induction and more effective modulation of radioiodine uptake in dedifferentiated thyroid cancer cells and in their distant metastatic lesions.
İyot (I-), tiroid bezi kaynaklı hormonlar olan triiodotironin (T3) ve tiroksinin (T4) temel bileşenlerindendir, ve tiroid bezinde iyodun derişimini artıran moleküler mekanizmalar aynı zamanda bu hormonların sentezlenmesinde de anahtar rol oynarlar. Bunun yanı sıra, radyoaktif özellikler gösteren iyot izotoplarının normal ve neoplastik dokulara taşınma kinetiklerindeki farklılıklar, bu radyoizotopların tiroid kanserinin teşhis ve tedavisinde etkili olarak kullanılmalarına yol açmıştır. Tiroid bezinde bulunan bu sodium gradyanına eşlenmiş iyot taşıma aktivitesi, temel olarak tiroid folikül hücrelerinin bazolateral hücre zarında bulunan Na+/I- simporter (NIS) proteininin işlevsel ifadesine bağlıdır. Bu derlemede, NIS proteininin yapısı, işlevi ve transkripsiyon ve translasyon sonrası çeşitli moleküler mekanizmalar ile düzenlenmesinin moleküler belirleyicileri özetlenmiştir. Sağlıklı ve kanserleşme özelliği taşıyan tiroid dokularında NIS düzenlenmesinin moleküler detayları daha iyi ve daha detaylı şekilde anlaşıldıkça, hem genetik ve hem de protein düzeyinde NIS’in radyoiyot taşıma etkinliğini düzenleyecek yeni küçük moleküllerin tanımlanabileceğini, bunların klinik uygulamalara aktarılmasının ise özellikle dedifferansiye olmuş tiroid kanseri ve metastazlarının teşhis ve tedavisinde yenilikçi ve etkili uygulamalara yol açacağını öne sürüyoruz.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest was declared by the authors. Financial Disclosure: The authors declared that this study has received no financial support.
Figures
References
-
- Wolff J. Transport of iodide and other anions in the thyroid gland. Physiol Rev. 1964;44:45–90. - PubMed
-
- Stubbe P, Schulte FJ, Heidemann P. Iodine deficiency and brain development. Bibl Nutr Dieta. 1986;38:206–208. - PubMed
-
- Carrasco N. Iodide transport in the thyroid gland. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993;1154:65–82. - PubMed
-
- Brown-Grant K. Extrathyroidal iodide concentrating mechanisms. Physiol Rev. 1961;41:189–213.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
