A new serotonin 5-HT6 receptor antagonist with procognitive activity - Importance of a halogen bond interaction to stabilize the binding
- PMID: 28117458
- PMCID: PMC5259792
- DOI: 10.1038/srep41293
A new serotonin 5-HT6 receptor antagonist with procognitive activity - Importance of a halogen bond interaction to stabilize the binding
Abstract
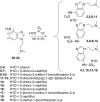
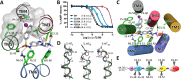
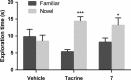
Serotonin 5-HT6 receptor has been proposed as a promising therapeutic target for cognition enhancement though the development of new antagonists is still needed to validate these molecules as a drug class for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and other pathologies associated with memory deficiency. As part of our efforts to target the 5-HT6 receptor, new benzimidazole-based compounds have been designed and synthesized. Site-directed mutagenesis and homology models show the importance of a halogen bond interaction between a chlorine atom of the new class of 5-HT6 receptor antagonists identified herein and a backbone carbonyl group in transmembrane domain 4. In vitro pharmacological characterization of 5-HT6 receptor antagonist 7 indicates high affinity and selectivity over a panel of receptors including 5-HT2B subtype and hERG channel, which suggests no major cardiac issues. Compound 7 exhibited in vivo procognitive activity (1 mg/kg, ip) in the novel object recognition task as a model of memory deficit.
Figures



References
-
- Codony X., Vela J. M. & Ramirez M. J. 5-HT6 receptor and cognition. Curr Opin Pharmacol 11, 94–100 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Fone K. C. F. An update on the role of the 5-hydroxytryptamine6 receptor in cognitive function. Neuropharmacology 55, 1015–1022 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Meneses A., Perez-Garcia G., Ponce-Lopez T. & Castillo C. 5-HT6 receptor memory and amnesia: behavioral pharmacology - learning and memory processes. International review of neurobiology 96, 27–47 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Benhamu B., Martin-Fontecha M., Vazquez-Villa H., Pardo L. & Lopez-Rodriguez M. L. Serotonin 5-HT6 receptor antagonists for the treatment of cognitive deficiency in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Med. Chem. 57, 7160–7181 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

