Impact of Antibodies That React With Liver Tissue and Donor-Specific Anti-HLA Antibodies in Pediatric Idiopathic Posttransplantation Hepatitis
- PMID: 28118175
- PMCID: PMC5642348
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001653
Impact of Antibodies That React With Liver Tissue and Donor-Specific Anti-HLA Antibodies in Pediatric Idiopathic Posttransplantation Hepatitis
Abstract
Background: The cause of late graft dysfunction has not been elucidated. Although an antibody-mediated reaction is suspected as a potential mechanism, the target antigens have not been clarified.
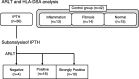
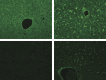
Methods: To clarify the etiology of idiopathic posttransplantation hepatitis (IPTH), we simultaneously examined the presence of antibodies that react with liver tissue (ARLT) by means of indirect immunofluorescence staining, as well as the presence of donor-specific anti-human leukocyte antigen antibodies (HLA-DSA). A subanalysis of the IPTH group was also performed. Within the IPTH group, the correlation between ARLT titer and clinical data were analyzed.
Results: In the sera of patients with IPTH (30 patients), ARLT were found at a significantly higher frequency than in patients without IPTH (42 patients; P < 0.001). Moreover, the ARLT titer appeared to be correlated with the severity of hepatitis or hepatic injury. In contrast, the frequency of HLA-DSA was significantly lower in patients with IPTH than in patients without IPTH (P = 0.001).
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that ARLT, and not HLA-DSA, profoundly influence the etiology of IPTH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Evans HM, Kelly DA, McKiernan PJ, et al. Progressive histological damage in liver allografts following pediatric liver transplantation. Hepatology. 2006;43:1109–1117. - PubMed
-
- Banff Working G, Demetris AJ, Adeyi O, et al. Liver biopsy interpretation for causes of late liver allograft dysfunction. Hepatology. 2006;44:489–501. - PubMed
-
- Fiel MI, Agarwal K, Stanca C, et al. Posttransplant plasma cell hepatitis (de novo autoimmune hepatitis) is a variant of rejection and may lead to a negative outcome in patients with hepatitis C virus. Liver Transpl. 2008;14:861–871. - PubMed
-
- Desai M, Neuberger J. Chronic liver allograft dysfunction. Transplant Proc. 2009;41:773–776. - PubMed
-
- Scheenstra R, Peeters PM, Verkade HJ, et al. Graft fibrosis after pediatric liver transplantation: ten years of follow-up. Hepatology. 2009;49:880–886. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

