Brief Report: Treatment of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Transgenic Mice With Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Restores Lymphatic Contractions, Repairs Lymphatic Vessels, and May Increase Monocyte/Macrophage Egress
- PMID: 28118521
- PMCID: PMC5449211
- DOI: 10.1002/art.40047
Brief Report: Treatment of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Transgenic Mice With Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Restores Lymphatic Contractions, Repairs Lymphatic Vessels, and May Increase Monocyte/Macrophage Egress
Abstract
Objective: Recent studies have demonstrated that there is an inverse relationship between lymphatic egress and inflammatory arthritis in affected joints. As a model, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-transgenic mice develop advanced arthritis following draining lymph node (LN) collapse, and loss of lymphatic contractions downstream of inflamed joints. It is unknown if these lymphatic deficits are reversible. This study was undertaken to test the hypothesis that anti-TNF therapy reduces advanced erosive inflammatory arthritis, associated with restoration of lymphatic contractions, repair of damaged lymphatic vessels, and evidence of increased monocyte egress.
Methods: TNF-transgenic mice with advanced arthritis and collapsed popliteal LNs were treated with anti-TNF monoclonal antibody (10 mg/kg weekly) or placebo for 6 weeks, and effects on knee synovitis, lymphatic vessel ultrastructure and function, and popliteal LN cellularity were assessed by ultrasound, histology, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), near-infrared indocyanine green imaging, and flow cytometry.
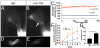
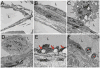
Results: Anti-TNF therapy significantly decreased synovitis (∼5-fold; P < 0.05 versus placebo), restored lymphatic contractions, and significantly increased the number of popliteal LN monocyte/macrophages (∼2-fold; P < 0.05 versus placebo). TEM demonstrated large activated macrophages attached to damaged lymphatic endothelium in mice with early arthritis, extensively damaged lymphatic vessels in placebo-treated mice with advanced arthritis, and rolling leukocytes in repaired lymphatic vessels in mice responsive to anti-TNF therapy.
Conclusion: These findings support the concept that anti-TNF therapy ameliorates erosive inflammatory arthritis, in part via restoration of lymphatic vessel contractions and potential enhancement of inflammatory cell egress.
© 2017, American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Efficacy of B cell depletion therapy for murine joint arthritis flare is associated with increased lymphatic flow.Arthritis Rheum. 2013 Jan;65(1):130-8. doi: 10.1002/art.37709. Arthritis Rheum. 2013. PMID: 23002006 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of the use of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) inhibitors, adalimumab and infliximab, for Crohn's disease.Health Technol Assess. 2011 Feb;15(6):1-244. doi: 10.3310/hta15060. Health Technol Assess. 2011. PMID: 21291629 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The role of vascular and lymphatic networks in bone and joint homeostasis and pathology.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 11;15:1465816. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1465816. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39324127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maackia amurensis seed lectin (MASL) ameliorates articular cartilage destruction and increases movement velocity of mice with TNFα induced rheumatoid arthritis.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022 Sep 9;32:101341. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101341. eCollection 2022 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022. PMID: 36120492 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Manual Lymphatic Drainage on the Concentrations of Selected Adipokines, Cytokines, C-Reactive Protein and Parameters of Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism in Patients with Abnormal Body Mass Index: Focus on Markers of Obesity and Insulin Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 19;24(12):10338. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210338. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373485 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell transcriptomics of popliteal lymphatic vessels and peripheral veins reveals altered lymphatic muscle and immune cell populations in the TNF-Tg arthritis model.Arthritis Res Ther. 2022 Mar 7;24(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02730-z. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35255954 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphatic Function in Autoimmune Diseases.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 20;10:519. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00519. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30949174 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smeets TJ, Kraan MC, van Loon ME, Tak PP. Tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade reduces the synovial cell infiltrate early after initiation of treatment, but apparently not by induction of apoptosis in synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(8):2155–62. - PubMed
-
- Wijbrandts CA, Remans PH, Klarenbeek PL, Wouters D, van den Bergh Weerman MA, Smeets TJ, et al. Analysis of apoptosis in peripheral blood and synovial tissue very early after initiation of infliximab treatment in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(11):3330–9. - PubMed
-
- Polzer K, Baeten D, Soleiman A, Distler J, Gerlag DM, Tak PP, et al. Tumour necrosis factor blockade increases lymphangiogenesis in murine and human arthritic joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67(11):1610–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

