Effect of XingPiJieYu decoction on spatial learning and memory and cAMP-PKA-CREB-BDNF pathway in rat model of depression through chronic unpredictable stress
- PMID: 28118829
- PMCID: PMC5260079
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-016-1543-9
Effect of XingPiJieYu decoction on spatial learning and memory and cAMP-PKA-CREB-BDNF pathway in rat model of depression through chronic unpredictable stress
Abstract
Background: Depression is a mental disorder characterized by a pervasive low mood and loss of pleasure or interest in usual activities, and often results in cognitive dysfunction. The disturbance of cognitive processes associated with depression, especially the impairment of learning and memory, exacerbates illness and increases recurrence of depression. XingPiJieYu (XPJY) is one of the most widely clinical formulas of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and can improve the symptoms of depression, including learning and memory. However, its regulatory effects haven't been comprehensively studied so far. Recently, some animal tests have indicated that the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)-protein kinase A (PKA)-cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB)-brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) signaling pathway in hippocampus is closely related to depression and the pathogenesis of cognitive function impairments. The present study was performed to investigate the effect and mechanism of XPJY on depression and learning and memory in animal model.
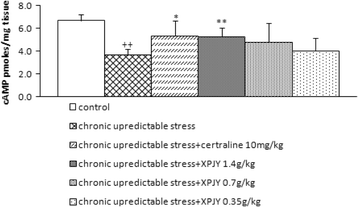
Materials: The rat model of depression was established by chronic unpredictable stress (CUS) for 21 days. The rats were randomly divided into six groups: control group, CUS group, CUS + XPJY (1.4 g/kg, 0.7 g/kg and 0.35 g/kg) groups, and CUS + sertraline (10 mg/kg) group. The sucrose preference, open field exploration and Morris water maze (MWM) were tested. The expression of cAMP, CREB, PKA and BDNF protein in hippocampus was examined with Elisa and Western Blot. The mRNA level of CREB and BDNF in hippocampus was measured with PCR.
Results: The results demonstrated that rats subjected to CUS exhibited decreases in sucrose preference, total ambulation, percentage of central ambulation, rearing in the open field test and spatial performance in the MWM. CUS reduced the expression of cAMP, PKA, CREB and BDNF in hippocampus of model rats. These effects could be reversed by XPJY.
Conclusion: The results indicated that XPJY can improve depression and related learning and memory and the effect of XPJY is partly exerted through the cAMP-PKA-CREB-BDNF signaling pathway.
Keywords: BDNF; CAMP; CREB; Chinese herbs; Chronic unpredictable stress; Depression; Learning and memory; PKA.
Figures



References
-
- Zakzanis KK, Leach L, Kaplan E. On the nature and pattern of neurocognitive function in major depressive disorder. Neuropsychiatry Neuropsychol Behav Neurol. 1998;11(11):111–119. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee R, Ghosh KA, et al. Stress. Negative Modulator of NGF. 2011;1(2):1–7.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

