The role of total cell-free DNA in predicting outcomes among trauma patients in the intensive care unit: a systematic review
- PMID: 28118843
- PMCID: PMC5260039
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-016-1578-9
The role of total cell-free DNA in predicting outcomes among trauma patients in the intensive care unit: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Cell-free DNA has been proposed as a means of predicting complications among severely injured patients. The purpose of this systematic review was to assess whether cell-free DNA was useful as a prognostic biomarker for outcomes in trauma patients in the intensive care unit.
Methods: We searched Pubmed, Embase, Scopus and the Cochrane Central Register for Controlled Trials and reference lists of relevant articles for studies that assessed the prognostic value of cell-free DNA detection in trauma patients in the intensive care unit. Outcomes of interest included survival, posttraumatic complications and severity of trauma. Due to considerable heterogeneity between the included studies, a checklist was formed to assess quality of cell-free DNA measurement.
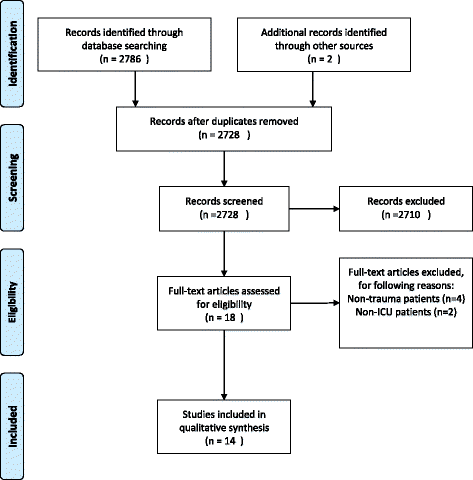
Results: A total of 14 observational studies, including 904 patients, were eligible for analysis. Ten studies were designed as prospective cohort studies; three studies included selected patients from a cohort while one study was of a retrospective design. We found a significant correlation between higher values of cell-free DNA and higher mortality. This significant correlation was evident as early as on intensive care unit admission. Likewise, cell-free DNA predicted the severity of trauma and posttraumatic complications in a majority of patients.
Conclusion: The amount of cell-free DNA can function as a prognostic tool for mortality and to a lesser extent severity of trauma and posttraumatic complications. Standardizing cell-free DNA measurement is paramount to ensure further research in cell-free DNA as a prognostic tool.
Keywords: Intensive care unit; Trauma; cfDNA; mtDNA; nDNA.
Figures
References
-
- Kim K, Shin DG, Park MK, Baik SH, Kim TH, Kim S, Lee S. Circulating cell-free DNA as a promising biomarker in patients with gastric cancer: diagnostic validity and significant reduction of cfDNA after surgical resection. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2014;86:136–42. doi: 10.4174/astr.2014.86.3.136. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Szpechcinski A, Chorostowska-Wynimko J, Struniawski R, Kupis W, Rudzinski P, Langfort R, Puscinska E, Bielen P, Sliwinski P, Orlowski T. Cell-free DNA levels in plasma of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and inflammatory lung disease. Br J Cancer. 2015;113:476–83. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.225. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reinert T, Scholer LV, Thomsen R, Tobiasen H, Vang S, Nordentoft I, Lamy P, Kannerup AS, Mortensen FV, Stribolt K, Hamilton-Dutoit S, Nielsen HJ, Laurberg S, Pallisgaard N, Pedersen JS, Orntoft TF, Andersen CL. Analysis of circulating tumour DNA to monitor disease burden following colorectal cancer surgery. Gut. 2016;65:625–34. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308859. - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Vlaminck I, Valantine HA, Snyder TM, Strehl C, Cohen G, Luikart H, Neff NF, Okamoto J, Bernstein D, Weisshaar D, Quake SR, Khush KK. Circulating cell-free DNA enables noninvasive diagnosis of heart transplant rejection. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6:241ra277. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3007803. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical