The Effectiveness and Safety of Topical Capsaicin in Postherpetic Neuralgia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 28119613
- PMCID: PMC5222862
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00538
The Effectiveness and Safety of Topical Capsaicin in Postherpetic Neuralgia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
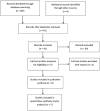
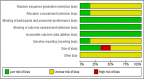
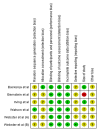
In particular, neuropathic pain is a major form of chronic pain. This type of pain results from dysfunction or lesions in the central and peripheral nervous system. Capsaicin has been traditionally utilized as a medicine to remedy pain. However, the effectiveness and safety of this practice is still elusive. Therefore, this systematic review aimed to investigate the effect of topical capsaicin as a pain-relieving agent that is frequently used in pain management. In brief, all the double-blinded, randomized placebo- or vehicle-controlled trials that were published in English addressing postherpetic neuralgia were included. Meta-analysis was performed using Revman® version 5.3. Upon application of the inclusion and exclusion criteria, only six trials fulfilled all the criteria and were included in the review for qualitative analysis. The difference in mean percentage change in numeric pain rating scale score ranges from -31 to -4.3. This demonstrated high efficacy of topical capsaicin application and implies that capsaicin could result in pain reduction. Furthermore, meta-analysis was performed on five of the included studies. All the results of studies are in favor of the treatment using capsaicin. The incidence of side effects from using topical capsaicin is consistently higher in all included studies, but the significance of safety data cannot be quantified due to a lack of p-values in the original studies. Nevertheless, topical capsaicin is a promising treatment option for specific patient groups or certain neuropathic pain conditions such as postherpetic neuralgia.
Keywords: Capsicum; capsaicin; pain; postherpetic neuralgia; topical agent.
Figures
References
-
- Backonja M. M., Malan T. P., Vanhove G. F., Tobias J. K. (2010). NGX-4010, a high-concentration capsaicin patch, for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized, double-blind, controlled study with an open-label extension. Pain Med. 11 600–608. 10.1111/j.1526-4637.2009.00793.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Basu S. K., Krishna A. D. (2003). “Capsicum: historical and botanical perspectives,” in Capsicum: The Genus Capsicum ed. Krishna A. D. (London: Taylor & Francis; ) 1–15.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources