Pneumoretroperitoneum, Pneumomediastinum, Subcutaneous Emphysema After a Rectal Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
- PMID: 28119867
- PMCID: PMC5256253
- DOI: 10.3393/ac.2016.32.6.234
Pneumoretroperitoneum, Pneumomediastinum, Subcutaneous Emphysema After a Rectal Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
Abstract
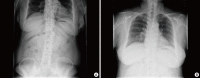
An endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) is an effective and safe therapeutic technique for treating a patient with a laterally-spreading tumor (LST). Colonoscopic-procedure-related complications are noted to be about 2.8% worldwide, and a perforation is the most common. Most colon perforations cause pneumoperitoneum. However, a perforation within the retroperitoneal portion of the colon (rectum and some of sigmoid colon) may cause an extraperitoneal perforation, and the leaking free air may induce pneumoretroperitoneum, pneumomediastinum, and subcutaneous emphysema, depending on the amount of discharged air. Herein, we present the case of a patient with an extraperitoneal colon microperforation which manifested as pneumoretroperitoneum, pneumomediastinum, and subcutaneous emphysema after an EMR for a sigmoid LST, which was successfully treated with medical treatment and endoscopic clipping.
Keywords: Colonoscopy; Perforation; Pneumomediastinum; Pneumoretroperitoneum; Subcutaneous emphysema.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


References
-
- Repici A, Pellicano R, Strangio G, Danese S, Fagoonee S, Malesci A. Endoscopic mucosal resection for early colorectal neoplasia: pathologic basis, procedures, and outcomes. Dis Colon Rectum. 2009;52:1502–1515. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka S, Haruma K, Oka S, Takahashi R, Kunihiro M, Kitadai Y, et al. Clinicopathologic features and endoscopic treatment of superficially spreading colorectal neoplasms larger than 20 mm. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;54:62–66. - PubMed
-
- Oka S, Tanaka S, Kanao H, Ishikawa H, Watanabe T, Igarashi M, et al. Current status in the occurrence of postoperative bleeding, perforation and residual/local recurrence during colonoscopic treatment in Japan. Dig Endosc. 2010;22:376–380. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

