A somatic GNA11 mutation is associated with extremity capillary malformation and overgrowth
- PMID: 28120216
- PMCID: PMC5511772
- DOI: 10.1007/s10456-016-9538-1
A somatic GNA11 mutation is associated with extremity capillary malformation and overgrowth
Abstract
Background: Capillary malformation is a cutaneous vascular anomaly that is present at birth, darkens over time, and can cause overgrowth of tissues beneath the stain. The lesion is caused by a somatic activating mutation in GNAQ. In a previous study, we were unable to identify a GNAQ mutation in patients with a capillary malformation involving an overgrown lower extremity. We hypothesized that mutations in GNA11 or GNA14, genes closely related to GNAQ, also may cause capillary malformations.
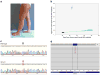
Methods: Human capillary malformation tissue obtained from 8 patients that had tested negative for GNAQ mutations were studied. Lesions involved an extremity (n = 7) or trunk (n = 1). Droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) was used to detect GNA11 or GNA14 mutant cells (p.Arg183) in the specimens. Single molecule molecular inversion probe sequencing (smMIP-seq) was performed to search for other mutations in GNA11. Mutations were validated by subcloning and sequencing amplimers.
Results: We found a somatic GNA11 missense mutation (c.547C > T; p.Arg183Cys) in 3 patients with a diffuse capillary malformation of an extremity. Mutant allelic frequencies ranged from 0.3 to 5.0%. GNA11 or GNA14 mutations were not found in 5 affected tissues or in unaffected tissues (white blood cell DNA).
Conculsions: GNA11 mutations are associated with extremity capillary malformations causing overgrowth. Pharmacotherapy that affects GNA11 signaling may prevent the progression of capillary malformations.
Keywords: Capillary malformation; Extremity; GNA11; GNAQ; Vascular anomaly.
Figures
References
-
- Nakashima M, Miyajima M, Sugano H, et al. The somatic GNAQ mutation c.548G>A (p. R183Q) is consistently found in Sturge-Weber syndrome. J Hum Genet. 2014;59:691–3. - PubMed
-
- Lee MS, Liang MG, Mulliken JB. Diffuse capillary malformation with overgrowth: a clinical subtype of vascular anomalies with hypertrophy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:589–94. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

