Childhood recurrent pneumonia caused by endobronchial sutures: A case report
- PMID: 28121955
- PMCID: PMC5287979
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005992
Childhood recurrent pneumonia caused by endobronchial sutures: A case report
Abstract
Background: Recurrent pneumonia is defined as more than two episodes of pneumonia in one year or three or more episodes anytime in life. Common clinical scenarios leading to recurrent pneumonia include anatomical abnormalities of respiratory tract, immunodeficiency, congenital heart diseases, primary ciliary dyskinesia, etc.
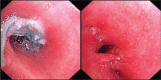
Case report: A school-aged girl suffered from 1-2 episodes of pneumonia each year after trachea connection and lung repair operation resulted from an accident of car crash. Bronchoscopy revealed the sutures twisted with granulation in the left main bronchus and the patient's symptoms relieved after removal of the sutures. Here we report for the first time that surgical suture was the cause of recurrent pneumonia.
Conclusions: This case indicates that children with late and recurrent onset of pneumonia should undergo detailed evaluation including bronchoscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Hoving MF, Brand PL. Causes of recurrent pneumonia in children in a general hospital. J Paediatr Child Health 2013;49:E208–12. - PubMed
-
- Owayed AF, Campbell DM, Wang EE. Underlying causes of recurrent pneumonia in children. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2000;154:190–4. - PubMed
-
- Lodha R, Puranik M, Natchu UC, et al. Recurrent pneumonia in children: clinical profile and underlying causes. Acta Paediatr (Oslo, Norway: 1992) 2002;91:1170–3. - PubMed
-
- Ciftci E, Gunes M, Koksal Y, et al. Underlying causes of recurrent pneumonia in Turkish children in a university hospital. J Trop Pediatr 2003;49:212–5. - PubMed
-
- Cabezuelo Huerta G, Vidal Mico S, Abeledo Gomez A, et al. Underlying causes of recurrent pneumonia. Anal Pediatr (Barcelona, Spain: 2003) 2005;63:409–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical