Cytoprotective effect of chlorogenic acid against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in MC3T3-E1 cells through PI3K/Akt-mediated Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- PMID: 28122344
- PMCID: PMC5362435
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14747
Cytoprotective effect of chlorogenic acid against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in MC3T3-E1 cells through PI3K/Akt-mediated Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
Abstract
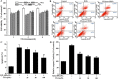
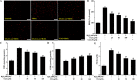
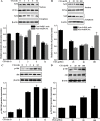
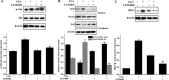
Osteoporosis is a disorder of bone and its development is closely associated with oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species (ROS). Chlorogenic acid (CGA) has potential antioxidant effects and its pharmacological action in osteoblasts is not clearly understood. The present study aimed to clarify the protective effects and mechanisms of CGA on hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced oxidative stress in osteoblast cells. MC3T3-E1 cells were treated with H2O2 to induce oxidative stress model in vitro. Cells were treated with CGA prior to H2O2 exposure, the intracellular ROS production, malondialdehyde content, nitric oxide release and glutathione level were measured. We also investigated the protein levels of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), the nuclear translocation of transcription factor NF-erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2) and the phosphorylation levels of Akt in CGA-treated cells. The results showed that pretreatment of CGA could reverse the inhibition of cell viability and suppress the induced apoptosis and caspase-3 activity. Additionally, it significantly reduced H2O2-induced oxidative damage in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, it induced the protein expression of HO-1 together with its upstream mediator Nrf2, and activated the phosphorylation of Akt in MC3T3-E1 cells. LY294002, a PI3K/Akt inhibitor, significantly suppressed the CGA-induced Nrf2 nuclear translocation and HO-1 expression. Reduction of cell death mediated by CGA in presence of H2O2 was significantly inhibited by Zinc protoporphyrin IX (a HO-1 inhibitor) and LY294002. These data demonstrated that CGA protected MC3T3-E1 cells against oxidative damage via PI3K/Akt-mediated activation of Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, which may be an effective drug in treatment of osteoporosis.
Keywords: MC3T3-E1 cells; Nrf2/HO-1 pathway; chlorogenic acid; cytoprotection; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Baek KH, Oh KW, Lee WY, Lee SS, Kim MK, Kwon HS, Rhee EJ, Han JH, Song KH, Cha BY, Lee KW, Kang MI. Association of oxidative stress with postmenopausal osteoporosis and the effects of hydrogen peroxide on osteoclast formation in human bone marrow cell cultures. Calcif Tissue Int. 2010;87:226–235. - PubMed
-
- Cervellati C, Bergamini CM. Oxidative damage and the pathogenesis of menopause related disturbances and diseases. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2015;54:739–753. - PubMed
-
- Liu YJ, Zhou CY, Qiu CH, Lu XM, Wang YT. Chlorogenic acid induced apoptosis and inhibition of proliferation in human acute promyelocytic leukemia HL60 cells. Mol Med Rep. 2013;8:1106–1110. - PubMed
-
- Arai M, Shibata Y, Pugdee K, Abiko Y, Ogata K. Effects of reactive oxygen species (ROS) on antioxidant system and osteoblastic differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells. IUBMB Life. 2007;59:27–33. - PubMed
-
- Pisoschi AM, Pop A. The role of antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: A review. Eur J Med Chem. 2015;97:55–74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

