Cytological diagnosis of Rosai-Dorfman disease: A case report and revision of the literature
- PMID: 28123703
- PMCID: PMC5244775
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2016.814
Cytological diagnosis of Rosai-Dorfman disease: A case report and revision of the literature
Abstract
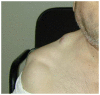
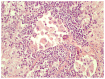
Rosai-Dorfman disease also known as sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (SHML) is characterized by distorted lymph node architecture with marked dilation of lymphatic sinuses occupied by numerous lymphocytes, as well as histiocytes with vesicular nucleus and abundant clear cytoplasm with phagocytized lymphocytes or plasma cells, also known as 'emperipolesis'. This disease of unknown etiology progresses with a benign prognosis strictly and only when an early diagnosis and treatment is made. A late diagnosis and a generalized lymph node involvement contribute to a poor prognosis. In this study, we focussed on the cytological characteristics of the Rosai-Dorfman disease and differential diagnoses. We reported a case of a 61-year-old Mexican male with a 9-month history of painless bilateral cervical masses and low-grade fever with the final diagnosis of Rosai-Dorfman disease. The final diagnosis was made by fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy of parotid gland and cervical lymph node. In conclusion, FNA biopsy can be enough to make the diagnosis in most cases due to the distinct cytological features of SHML, thereby avoiding more invasive approaches that potentially are unnecessary.
Keywords: Rosai-Dorfman disease; fine needle aspiration biopsy; massive lymphadenopathy; sinus histiocytosis.
Figures


References
-
- Foucar E, Rosai J, Dorfman R. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease): Review of the entity. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1990;7:19–73. - PubMed
-
- Gaitonde S. Multifocal, extranodal sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy: An overview. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007;131:1117–1121. - PubMed
-
- Cocker RS, Kang J, Kahn LB. Rosai-Dorfman disease. Report of a case presenting as a midline thyroid mass. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2003;127:e197–e200. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
