Association between the rs1805081 polymorphism of Niemann-Pick type C1 gene and cardiovascular disease in a sample of an Iranian population
- PMID: 28123713
- PMCID: PMC5244780
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2016.802
Association between the rs1805081 polymorphism of Niemann-Pick type C1 gene and cardiovascular disease in a sample of an Iranian population
Abstract
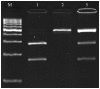
The aim of the present study was to investigate the association between a genetic variation, A+644G, in the Niemann-Pick type C1 (NPC1) gene and the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in a Southeast Iranian population. A total of 320 individuals, including 200 patients with CVD and 120 healthy individuals, were involved in the present study. The polymorphism was determined using a polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism method. The results indicated that the frequency of the GG genotype was markedly lower in patients with CVD compared with the control group (7 vs. 16.7%), and that the NPC1 rs1805081 polymorphism was associated with reduced risk of CVD [odds ratio (OR)=0.110; 95% confidence interval (CI)=0.017-0.715; P=0.021]. In addition, the prevalence of the minor allele (G) in patients with CVD differed from that of the control group with the frequency of 25.5 and 33.4% for the former and latter, respectively, and this difference reached statistical significance (OR=0.658; 95% CI=0.482-0.971; P=0.037). Furthermore, analysis of clinical characteristics of the individuals according to the NPC1 genotypes revealed an association between the lipid profile and NPC1 gene polymorphism. These findings demonstrated that the NPC1 A+644G variant was associated with reduced risk of CVD and serves a protective role against susceptibility to CVD in the Iranian population.
Keywords: NPC1; cardiovascular disease; genetic polymorphism.
Figures
References
-
- Chapman MJ, Ginsberg HN, Amarenco P, Andreotti F, Borén J, Catapano AL, Descamps OS, Fisher E, Kovanen PT, Kuivenhoven JA, et al. European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel: Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease: Evidence and guidance for management. Eur Heart J. 2011;32:1345–1361. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources