Zonulin, a regulator of epithelial and endothelial barrier functions, and its involvement in chronic inflammatory diseases
- PMID: 28123927
- PMCID: PMC5214347
- DOI: 10.1080/21688370.2016.1251384
Zonulin, a regulator of epithelial and endothelial barrier functions, and its involvement in chronic inflammatory diseases
Abstract
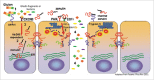
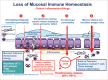
Beside digesting nutrients and absorbing solutes and electrolytes, the intestinal epithelium with its barrier function is in charge of a tightly controlled antigen trafficking from the intestinal lumen to the submucosa. This trafficking dictates the delicate balance between tolerance and immune response causing inflammation. Loss of barrier function secondary to upregulation of zonulin, the only known physiological modulator of intercellular tight junctions, leads to uncontrolled influx of dietary and microbial antigens. Additional insights on zonulin mechanism of action and the recent appreciation of the role that altered intestinal permeability can play in the development and progression of chronic inflammatory disorders has increased interest of both basic scientists and clinicians on the potential role of zonulin in the pathogenesis of these diseases. This review focuses on the recent research implicating zonulin as a master regulator of intestinal permeability linked to the development of several chronic inflammatory disorders.
Keywords: autoimmune disease; barrier function; intestinal permeability; tight junctions; zonulin.
Figures
References
-
- Arrieta MC, Bistritz L, Meddings JB. Alterations in intestinal permeability. Gut 2006; 55:1512-20; PMID:16966705; http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/gut.2005.085373 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fasano A, Shea-Donohue T. Mechanisms of disease: the role of intestinal barrier function in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal autoimmune diseases. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005; 2:416-22; PMID:16265432; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncpgasthep0259 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sapone A, de Magistris L, Pietzak M, Clemente MG, Tripathi A, Cucca F, Lampis R, Kryszak D, Cartenì M, Generoso M, et al.. Zonulin upregulation is associated with increased gut permeability in subjects with type 1 diabetes and their relatives. Diabetes 2006; 55:1443-9; PMID:16644703; http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/db05-1593 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bach JF. The effect of infections on susceptibility to autoimmune and allergic diseases. N Engl J Med 2002; 347:911-20; PMID:12239261; http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra020100 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Strachan DP. Hay fever, hygiene, and household size. BMJ 1989; 299:1259-60; PMID:2513902; http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.299.6710.1259 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
