Interictal brain activity differs in migraine with and without aura: resting state fMRI study
- PMID: 28124204
- PMCID: PMC5267588
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-016-0716-8
Interictal brain activity differs in migraine with and without aura: resting state fMRI study
Abstract
Background: Migraine is one of the most severe primary headache disorders. The nature of the headache and the associated symptoms during the attack suggest underlying functional alterations in the brain. In this study, we examined amplitude, the resting state fMRI fluctuation in migraineurs with and without aura (MWA, MWoA respectively) and healthy controls.
Methods: Resting state functional MRI images and T1 high-resolution images were acquired from all participants. For data analysis we compared the groups (MWA-Control, MWA-MWoA, MWoA-Control). The resting state networks were identified by MELODIC. The mean time courses of the networks were identified for each participant for all networks. The time-courses were decomposed into five frequency bands by discrete wavelet decomposition. The amplitude of the frequency-specific activity was compared between groups. Furthermore, the preprocessed resting state images were decomposed by wavelet analysis into five specific frequency bands voxel-wise. The voxel-wise amplitudes were compared between groups by non-parametric permutation test.
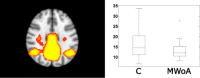
Results: In the MWA-Control comparison the discrete wavelet decomposition found alterations in the lateral visual network. Higher activity was measured in the MWA group in the highest frequency band (0.16-0.08 Hz). In case of the MWA-MWoA comparison all networks showed higher activity in the 0.08-0.04 Hz frequency range in MWA, and the lateral visual network in in higher frequencies. In MWoA-Control comparison only the default mode network revealed decreased activity in MWoA group in the 0.08-0.04 Hz band. The voxel-wise frequency specific analysis of the amplitudes found higher amplitudes in MWA as compared to MWoA in the in fronto-parietal regions, anterior cingulate cortex and cerebellum.
Discussion: The amplitude of the resting state fMRI activity fluctuation is higher in MWA than in MWoA. These results are in concordance with former studies, which found cortical hyperexcitability in MWA.
Keywords: ALFF; Frequency analysis; MRI; Migraine; Migraine with aura.
Figures


References
-
- Hadjikhani N, Sanchez Del Rio M, Wu O, Schwartz D, Bakker D, Fischl B, Kwong KK, Cutrer FM, Rosen BR, Tootell RB, Sorensen AG, Moskowitz MA. Mechanisms of migraine aura revealed by functional MRI in human visual cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:4687–4692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.071582498. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

